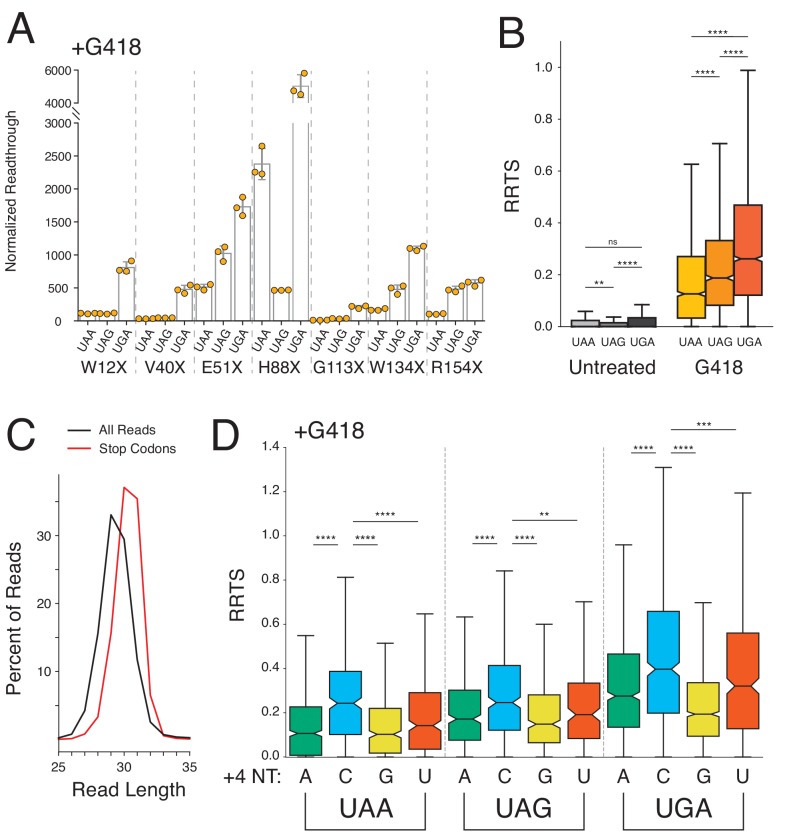
Figure 4. Stop codon identity influences readthrough probability genome-wide.
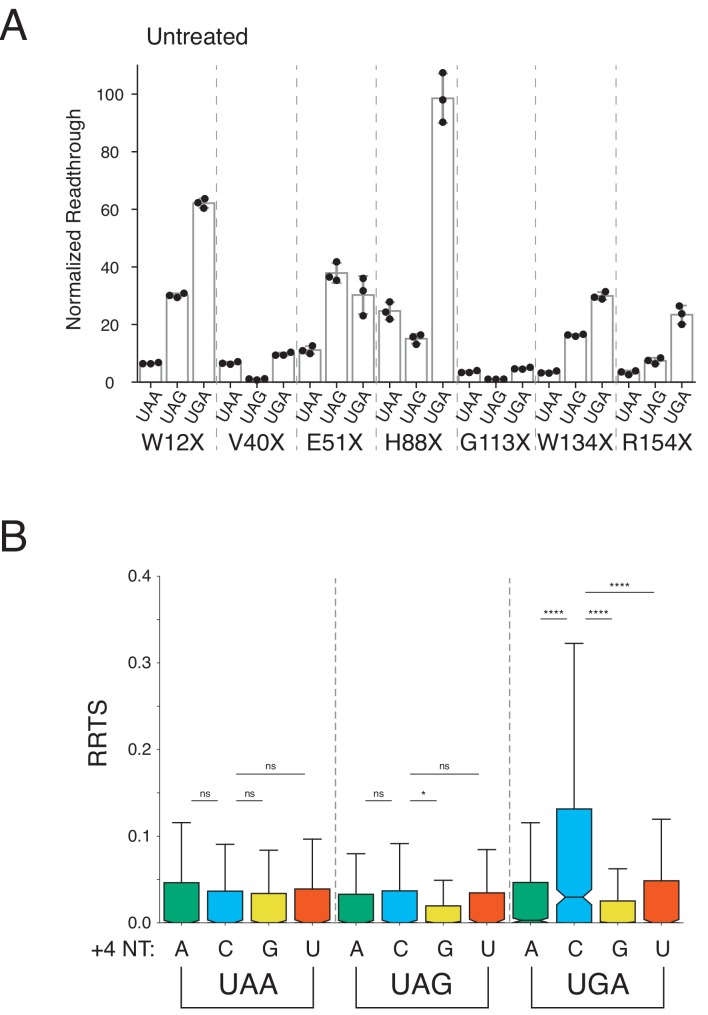
(A) Luciferase activity in HEK293T cells treated with 0.5 mg/mL G418 for 24 hr was measured for seven different PTCs (W12X, V40X, E51X, H88X, G113X, W134X, and R154X) in NLuc testing all three possible stop codons at each position. Normalized readthrough values - NLuc/FLuc ratios normalized to the lowest NLuc/FLuc ratio in untreated cells (Figure 4—figure supplement 1A, V40X-UAG), are plotted for each stop codon. Experiments were performed in triplicate with error bars representing one standard deviation. (B) Box and whisker plot showing RRTS values of transcripts sorted by NTC identity. Two-sided Mann-Whitney U tests were performed to test for significant differences between groups of transcripts. (C) Read size distributions comparing lengths of reads at stop codons (red) to all reads (black) in untreated cells. (D) Distribution of RRTS values, in G418-treated cells, comparing the effect of the 4 nt termination codon on readthrough. Within each 3 nt stop codon, presence of a C at the +4 position significantly increases RRTS values (One-sided Mann-Whitney U test, p<0.01 for all comparisons). Outliers are not shown.