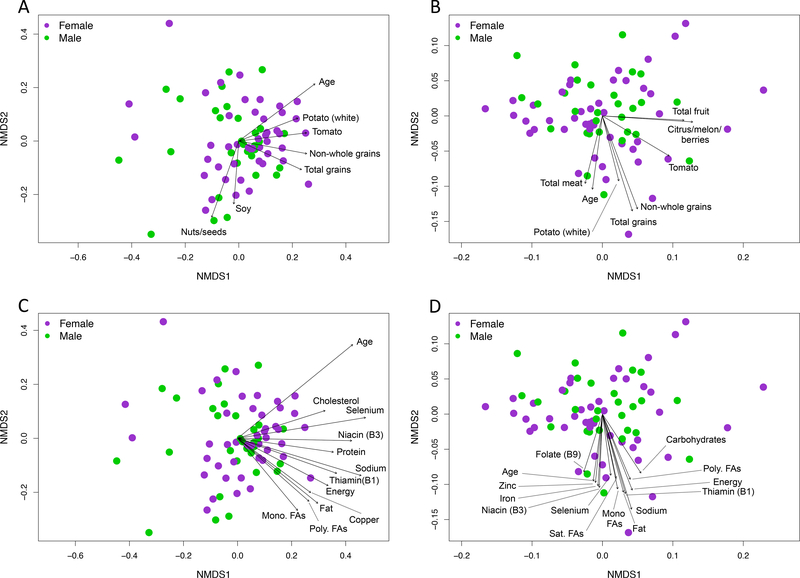
Figure 1.
Consumption of specific food groups (A & B) and nutrients (C & D) were strongly associated with gut microbiome membership (unweighted UniFrac, A & C) and structure (weighted UniFrac, B & D) in children aged 2–9 years. Each point in each non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plot represents the average microbiome composition of one child across three time points and are colored based on sex of the child. Vectors depict significant correlations (P ≤ 0.05) between specific dietary features and microbiome composition across the study population as determined from 10,000 permutations using the ‘envfit’ function in R vegan package. Text files of ‘envfit’ results are available online at figshare34.