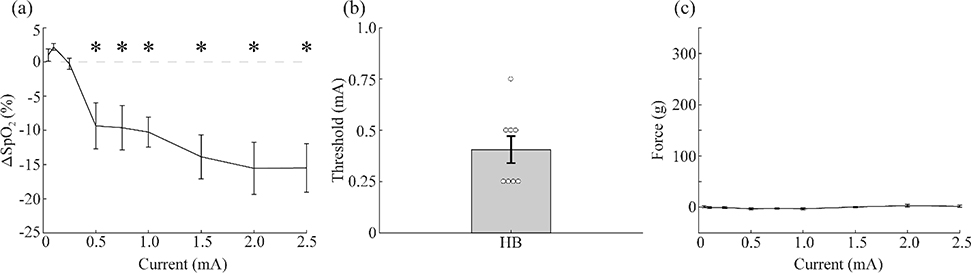
Figure 1: Implanted VNS activates the vagus nerve at low intensities.
a) VNS delivered via an implanted cuff electrode produces reductions in SpO2 as a function of stimulation intensity (n=8). b) The threshold intensity for generating a significant drop in SpO2 was approximately 0.5 mA. c) VNS delivered via an implanted cuff electrode produces minimal muscle activation as a function of stimulation intensity (n=8). * denotes intensities at which the mean response significantly differed from zero with p<0.05.