Figure 2. Dietary NR supplementation modestly extends survival in hSOD1G93A mice.
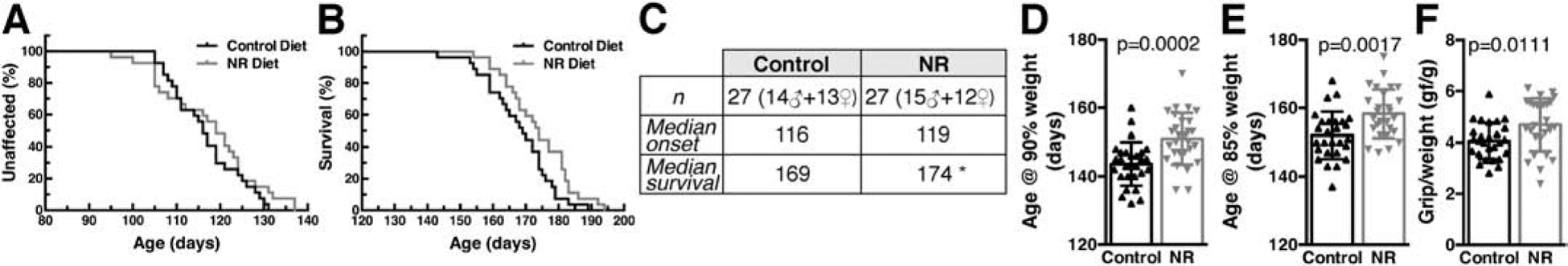
A) Disease onset in hSOD1G93A mice on control or nicotinamide riboside (NR)-supplemented diet. Onset was determined as the age at peak body weight. Curves are not significantly different. B) NR increased the median survival of hSOD1G93A mice from 169 days to 174 days. Survival curves are significantly different p<0.05 (Log-rank test, χ2=4.1). C) Summary of the data presented in (A) and (B) (*p<0.05). D) Age at which hSOD1G93A mice on control or NR-supplemented diet exhibited 10% weight loss (age at 90% of peak body weight, mean ± SD). E) Age at which hSOD1G93A mice on control or NR-supplemented diet exhibited 15% weight loss (age at 85% of peak body weight, mean ± SD). F) Ratio of hind-limb grip strength to body weight at 110 days of age in hSOD1G93A mice on control or NR-supplemented diet (mean ± SD). The number and sex of the animals for panels (D), (E) and (F) are the same as in (C).
