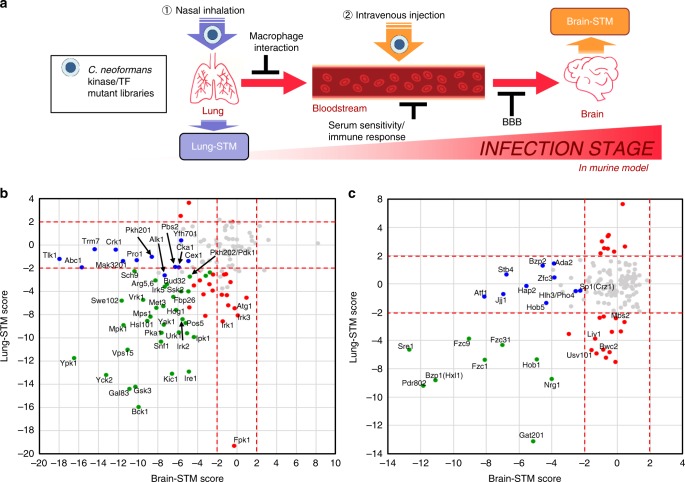
Fig. 1. Dual signature-tagged mutagenesis (STM) analyses of kinase and TF deletion libraries of C. neoformans.
(a) A schematic diagram for comparison of lung (via intranasal infection) and brain (via intravenous infection) STM analysis using C. neoformans TF and kinase mutant libraries15, 16. (b-c) Lung-STM scores for each mutant were obtained from the previous reports using a intranasally infected murine model (A/J mice, n = 3). Brain-STM scores were obtained in this study using the A/J mouse model intravenously infected with the same set of TF and kinase mutant libraries (the whole data were shown in Supplementary Fig. 2). Dual STM scores of (b) 129 kinases and (c) 155 TFs were represented by brain-STM score (X-axis) and lung-STM score (Y-axis). Each spot was an average STM score of two-independent TF or kinase mutant strains, each of which was obtained from three mice (n = 3). We used the colour code for kinase/TF mutants that exceeded STM cutoff [>2.0 (high) or < −2.0 (low)] and had statistically significant P values (<0.05) by one-way ANOVA analysis with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Green dots indicate the core-virulence kinase/TF mutants that show low/high STM scores in both lung- and brain infections. Blue dots indicate the kinase/TF mutants that show low/high STM scores only in brain-infection. Red dots indicate the kinase/TF mutants that show low/high STM only in lung infection.