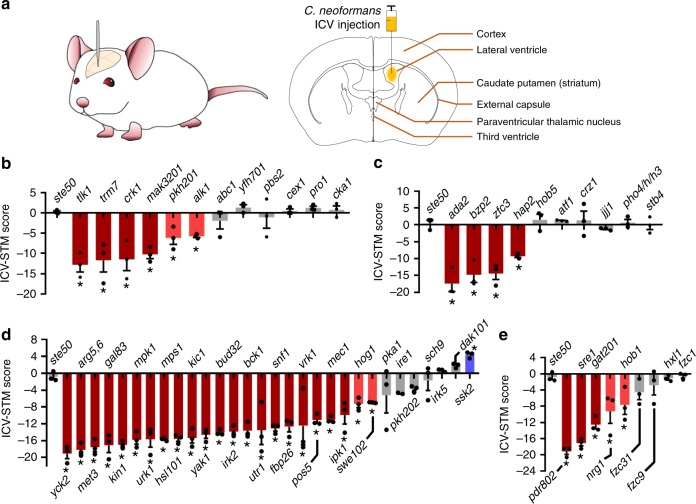
Fig. 4. Identification of genes required for survival of C. neoformans in the brain parenchyma through intracerebroventricular (ICV)-STM analysis.
(a) Graphical abstract of ICV injection for directly infecting the brain parenchyma with C. neoformans. (b–e) ICV-STM score of brain-infection-related (b) kinases, (c) TFs, core-virulence (d) kinases, and (e) TFs. Three mice (A/J) were infected with each pooled mutant group (Supplementary Data 4), sacrificed after 7 dpi, and infected brain tissues were harvested for recovering cryptococcal cells. The ICV-STM score was calculated by quantitative PCR of genomic DNA isolated from input and output cryptococcal mutants as described in Methods. The ste50Δ mutant was used as a virulent control strain. Red and blue marks (with *) indicate mutants whose STM scores are statistically different (P < 0.05, n = 3) from the ste50Δ STM score by one-way ANOVA analysis with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM.