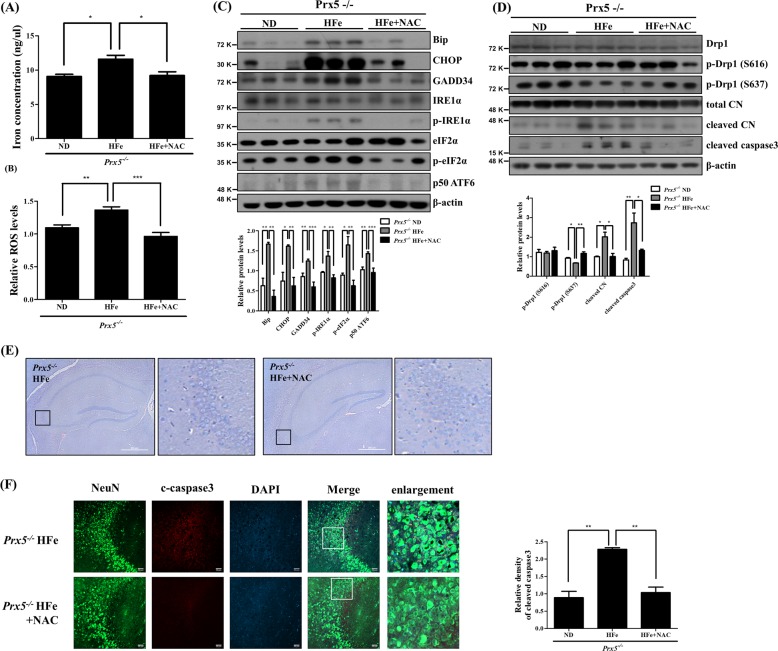
Fig. 7. NAC attenuates iron overload-induced hippocampal damage.
Iron-loaded Prx5−/− mice were treated with or without NAC (n = 3 per group). a The levels of iron concentration were quantified by an iron assay kit in hippocampal tissue. b Relative ROS levels were measured by the OxiSelect In Vitro ROS/RNS Assay Kit in hippocampal tissues. c The expression levels of Bip, CHOP, GADD34, IRE1α, phosphorylated IRE1α, eIF2α, phosphorylated eIF2α, and ATF6 were determined by western blotting. The graph shows the quantification of proteins/β-actin or phosphorylated protein/total protein. d The levels of Drp1, phosphorylated Drp1 (Ser637), phosphorylated Drp1 (Ser616), calcineurin, and cleaved caspase3 were assessed by western blotting. The graph shows the quantification of phosphorylated Drp1/Drp1, cleaved calcineurin/total calcineurin, and cleaved caspase3/β-actin. e Hippocampi were observed by H&E staining using an optical microscope. The second and fourth panels in each row show the magnified images of regions indicated by black squares in the first and third panels of each row, respectively; scale bar = 500 μm. f Immunohistochemistry images for NeuN (green), cleaved caspase3 (red), and DAPI (blue) were observed by confocal microscopy in hippocampi; scale bar = 50 μm. The graph shows the relative density of cleaved caspase3. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.