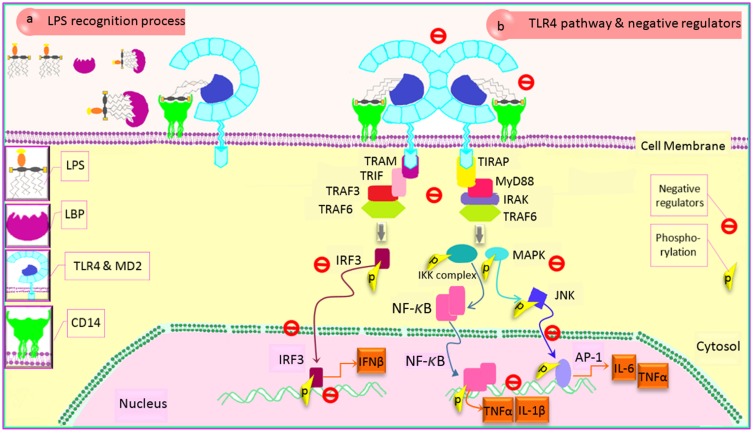
Figure 2.
LPS transferring pathway and modulation of TLR4 signaling cascade. (a) TLR4-MD2 complex and LPS recognizing: TLR4 signaling cascade is activated following LPS sensing mediated by three different protein activities, causing both ligand recognizing and transferring to receptor. The LBP-LPS complex is recognized by CD14, TLR4 co-receptor, leading to TLR4 cascade activation. (b) TLR4 protein adaptors and negative regulators: TLR4 signaling necessitates recruiting two main adaptors, including MyD88 and TRIF. Activation of other mediators causes the phosphorylation of some proteins which leads to the translocation of inflammatory transcription factors into nucleus, inducing effective inflammatory genes upregulation. Modulating of TLR4 is mediated by the negative regulator proteins in different stages (TLR4 sensing ligand, CD14, adaptor recruitment, transcriptional factor activation, transcriptional factor translocation, gene transcription) to either control the excessive response of TLR4 or suppress its activities at an effective time following an inflammatory response.
Abbreviations: TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LBP, LPS-binding protein; CD, cluster of differentiation; MD2, myeloid differentiation factor 2; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-β; TIRAP, TIR domain-containing adaptor protein; TRAM, TRIF-related adaptor molecule; IRAK, IL-1R-associated kinase; TRAF6, TNF-receptor-associated factor 6; IKK, inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells kinase; IL, interleukin; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; AP-1, activator protein 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; p, phosphorylation.