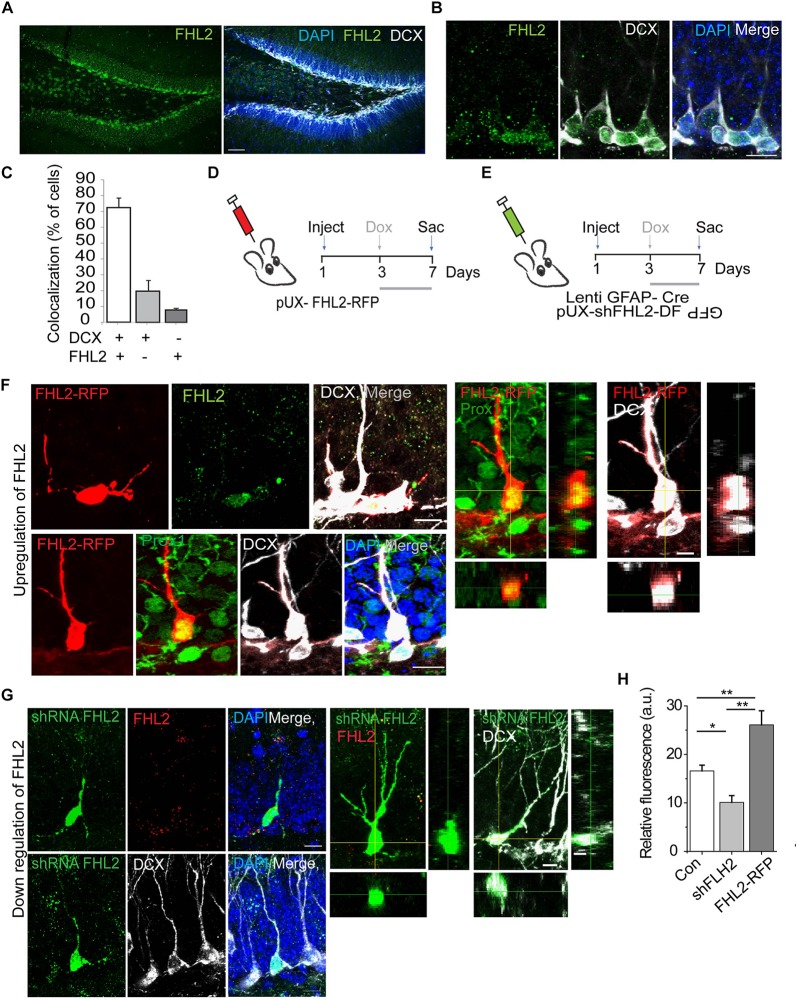
FIGURE 3.
Endogenous expression and successful manipulation of FHL2 in adult-born DGCs. (A) Representative coronal section of the DG immunolabeled with FHL2 and DCX. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Representative image of the dentate gyrus labeled with FHL2 colocalized with DCX. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of colocalization between DCX and FHL2 in the dentate gyrus. (D) Experimental timeline of inducible overexpression of FHL2 in adult-born DGCs with doxycycline induction (dox) at 3 dpi and sacrifice (sac) at 7 dpi. (E) Experimental timeline of inducible downregulation of FHL2 in adult-born DGCs with doxycycline induction (dox) at 3 dpi and sacrifice (sac) at 7 dpi. (F) Representative image of a newborn neuron at 7 dpi overexpressing FHL2 with FHL2 signal shown (top) and Prox 1 colocalization shown (bottom). Orthogonal views of the expression of Prox1 and DCX in RFP positive cells shown in the right panels. (G) Representative images of newborn neurons (DCX +) at 7 dpi with viral-mediated FHL2 knock-down. Orthogonal analysis of the expression of FHL2 and DCX colocalization shown in the right panels. (H) Quantification of relative fluorescence of FHL2 signal in control (con) newborn DGCs, shFHL2 cells, and FHL2-RFP cells (n = 103 cells) at 7 dpi. One-way ANOVA F(2,67) = 15.64, P < 0.0001. Followed by post hoc Tukey HSD tests, con vs. shFHL2, P = 0.037; con vs. FHL2-RFP, P < 0.01; shFHL2 vs. FHL2-RFP, P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01. Error bars, SEM. N = 3–4 mice per condition. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, Con, control.