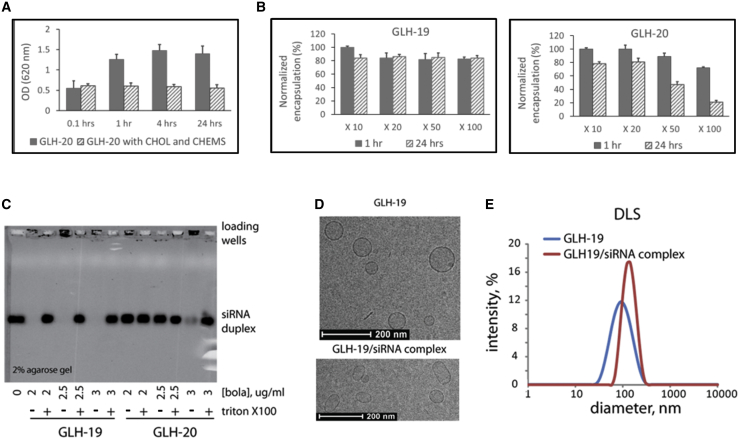
Figure 2.
Characterization of the Bola Vesicles in Terms of Stability, Affinity to siRNA, Morphology, and Size Distribution
(A) Stability of the vesicles in solution as measured by the development of turbidity due to vesicle aggregation. Vesicles were made from 10 mg/mL GLH-20 without CHOL and CHEMS (filled bars) and from 10 mg/mL GLH-20 with CHOL and CHEMS at a molar ratio of 2:1:1 (striated bars). Turbidity was measured by absorbance at 620 nm. (B) Stability of vesicles after dilution. Vesicles were prepared from 10 mg/mL GLH-19 (left panel) and GLH-20 (right panel) in PBS/10 buffer containing 0.1 mg/mL CF. Percent CF encapsulation was measured immediately (filled bars) and 24 h (striated bars) after dilution. A series of dilutions (10- to 100-fold) was done in PBS/10. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of GLH-19/siRNA and GLH-20/siRNA vesicles. siRNA (400 nM final concentration) was mixed with the bola at final amounts, which are indicated in the figure (in μg). For each amount of bola, 0.1% Triton X-100 was added in order to disintegrate the vesicles and release the encapsulated siRNA. (D) Cryo-TEM images of GLH-19 and GLH-19/siRNA vesicles. (E) Size distribution measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) indicates average diameters for GLH-19 and GLH-19/siRNA to be ∼85 and ∼125 nm, respectively. These sizes are in a good agreement with the observation made by the cryo-TEM. All tested bola vesicles in (B)–(E) contain CHOL and CHEMS. Note that all depicted error bars (A and B) represent the mean of 3 replicates + or - the standard deviation (SD).