Figure 2.
KLHDC1 Destabilizes Truncated SELENOS (SELENOS(ΔSec))
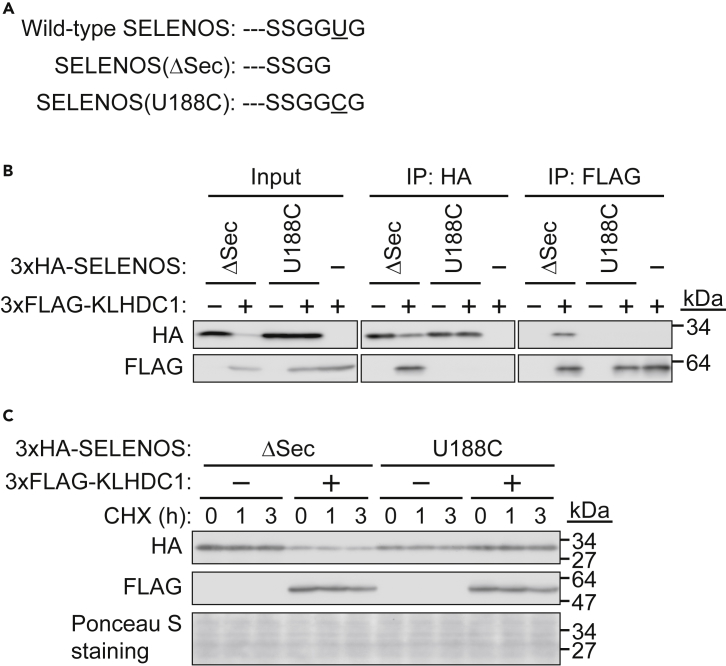
(A) Alignment of the C-terminal amino acid sequence of human SELENOS and mutants. Wild-type SELENOS contains selenocysteine (U) before the last glycine (G). SELENOS(ΔSec) is produced by failed U incorporation during protein translation and results in (A) -GG end. SELENOS(U188C) is generally utilized as wild-type SELENOS.
(B) KLHDC1 recognizes SELENOS(ΔSec) but not SELENOS(U188C). 3×HA-SELENOS(ΔSec) or SELENOS(U188C) was expressed in HEK293T cells, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with an anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody.
(C) SELENOS(ΔSec) is weakly expressed in the presence of KLHDC1. 3×HA-SELENOS(ΔSec) or SELENOS(U188C) was expressed in HEK293T cells with or without 3×FLAG-KLHDC1. The cells were exposed to cycloheximide (25 μg/mL) for 1 or 3 h, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting (IB) with an anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody. Ponceau S staining rather than a particular protein, such as tubulin or actin, was used as a loading control.