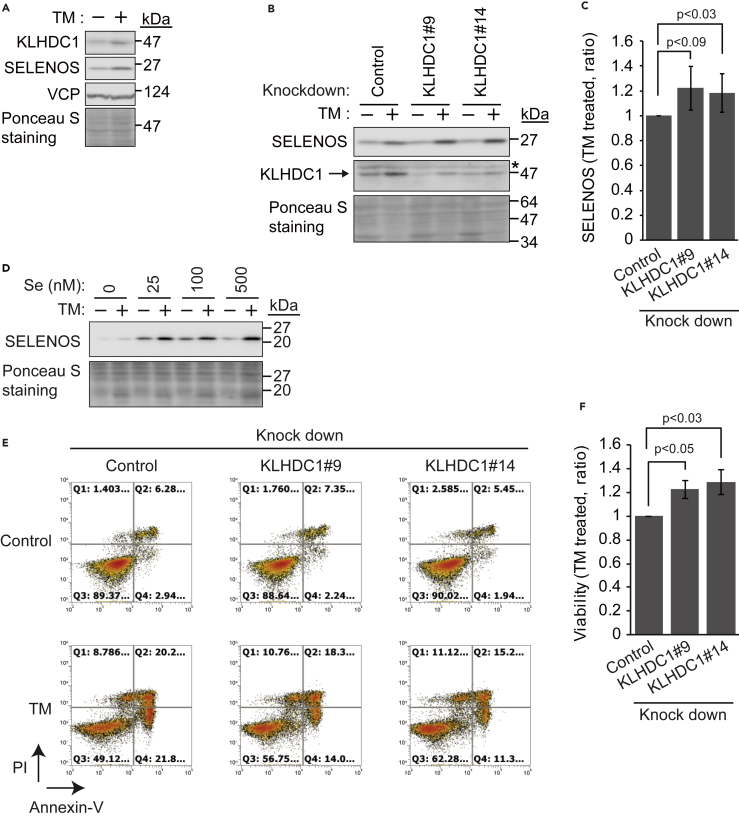
Figure 5.
KLHDC1 Enhances ER Stress-Induced U2OS Cell Death
(A) KLHDC1 is induced by tunicamycin (TM) treatment. U2OS cells were cultured in the presence or absence of TM (1 μg/mL) for 24 h, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting (IB) with an anti-KLHDC1, anti-SELENOS, or anti-VCP antibody. Ponceau S staining was used as a loading control.
(B) Control or KLHDC1-knockdown (#9 or #14) U2OS cells were treated with TM (1 μg/mL) for 24 h, and cell lysates were subjected to IB with an anti-KLHDC1 or anti-SELENOS antibody. Ponceau S staining was used as a loading control.
(C) Quantification of SELENOS expression in (B). SELENOS signals were normalized to those of ponceau S staining. Expression in control samples with TM treatment was set as 1. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
(D) U2OS cells were cultured without serum for 15 h. Then, medium was changed, and cells were incubated for 1 day with or without TM (1 μg/mL) and different concentrations of selenium in the absence of serum. Cell lysates were subjected to IB with an anti-SELENOS antibody. Ponceau S staining was used as a loading control.
(E) KLHDC1 knockdown partly prevents cell death induced by TM treatment. Control or KLHDC1-knockdown (#9 or #14) U2OS cells were treated with TM (1 μg/mL) for 24 h, and the cells were stained with propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin V and subjected to FACS analysis. PI-negative and Annexin V-negative populations represent viable cells. Cell numbers in Q1–4 indicate the cell population in each fraction. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown.
(F) Cell viability of control and KLHDC1-knockdown (#9 or #14) U2OS cells after TM treatment. The viability of control knockdown cells with TM treatment was set as 1. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance of differences was not considered, as described in the methods section.