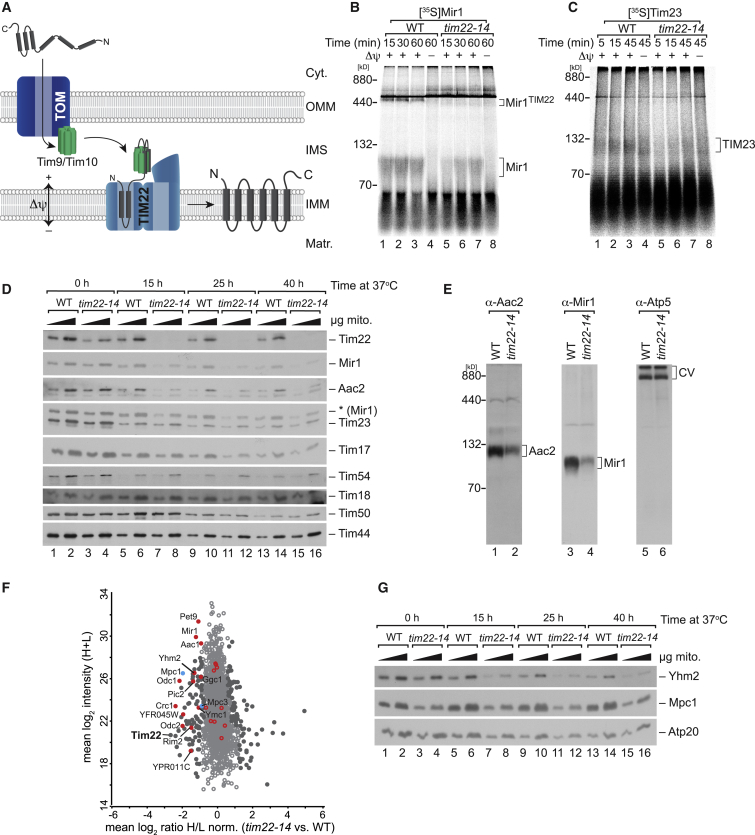
Figure 1.
tim22-14 Displays Defective Mitochondrial Carrier Protein Import under Non-permissive Conditions
(A) Hydrophobic proteins with internal signals translocate through the TOM complex. In the IMS, the small TIM complex directs cargo to the TIM22 complex for membrane potential-dependent membrane insertion.
(B and C) [35S]-labeled Mir1 (6TM) (B) and Tim23 (4TM) (C) were imported into wild-type (WT) and tim22-14 mitochondria. Membrane insertion was monitored by BN-PAGE and digital autoradiography.
(D) Mitochondria from cells grown at the non-permissive temperature for indicated times were analyzed by western blotting.
(E) WT and tim22-14 mitochondria from cells grown at 37°C for 15 h analyzed by BN-PAGE and immunodecoration.
(F) Proteomic analyses of tim22-14 versus WT mitochondria. Mean log2 ratio-intensity plot mitochondria are shown. The ratio-intensity mean plot shows the effect of loss of Tim22 function on the abundance of mitochondrial carrier proteins (in red, blue for MPC subunits). Filled circles indicate proteins significantly altered in abundance.
(G) Immunodetection of selected proteins in WT and tim22-14 mitochondria. Δψ, membrane potential; N, N terminus; C, C terminus; Cyt., cytoplasm; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; IMS, intermembrane space; Matr., matrix.