Figure 3.
Bronchial Lesions Share the Molecular Circuitry with Cisplatin-Resistant Alveolar Lesions
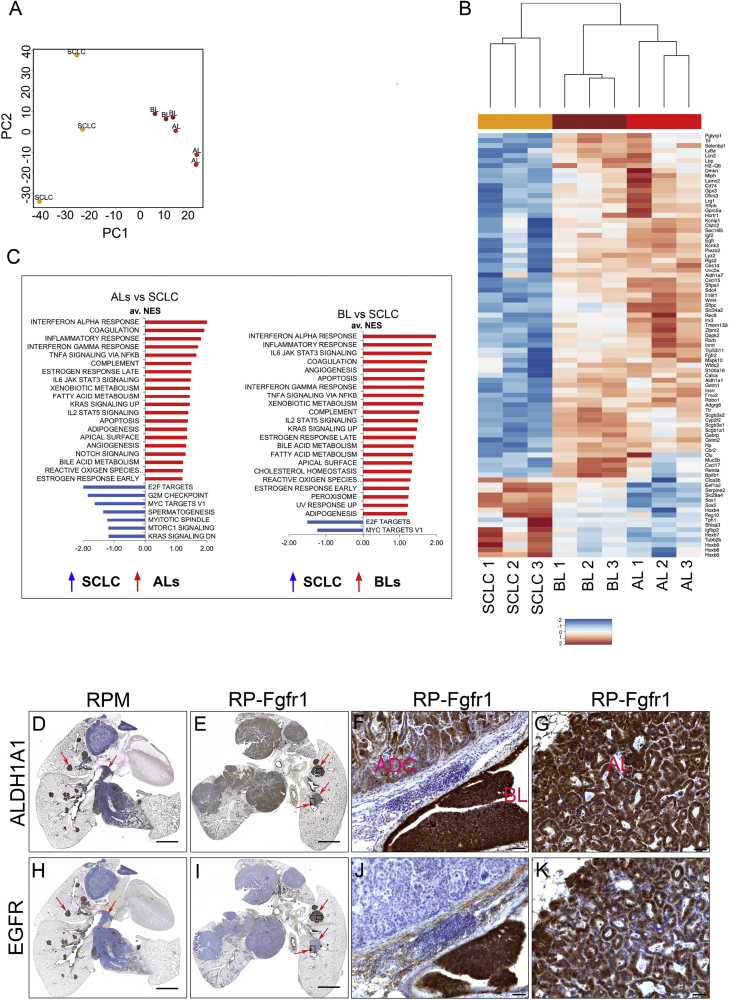
(A) Principal component analysis on triplicates of SCLC, BLs, and ALs samples. Plotted are the principle components 1 and 2 (PC1, PC2).
(B) Heatmap of genes with the highest rotation value for PC1.
(C) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) using the HALLMARKS gene sets of ALs versus SCLC (left graph) and BLs versus SCLC (right graph); FDR q value <0.25, normalized enrichment score (NES) ≥1.
(D–K) ALDH1A1 (D–G) and EGFR (H–K) staining on lung sections indicating whole lung of RP-Fgfr1 mice (E and I) and RPM mice as positive control (D and H) collected at humane endpoint. High magnification images of RP-Fgfr1 lungs show ALDH1A1 staining of ADC and BL (F) or AL (G) and EGFR staining of ADC and BL (J) or AL (K). Scale bars indicate 2 mm (D, E, H, and I) and 50 μm (F, G, J, and K). Arrows in (D) and (H) indicate central and peripheral lesions. Arrows in (E) and (I) indicate peripheral BL and AL lesions. Rectangles in (E) and (I) indicate regions that are shown with higher magnification in (F), (G), (J), and (K).
See also Figure S2.