Fig. 2.
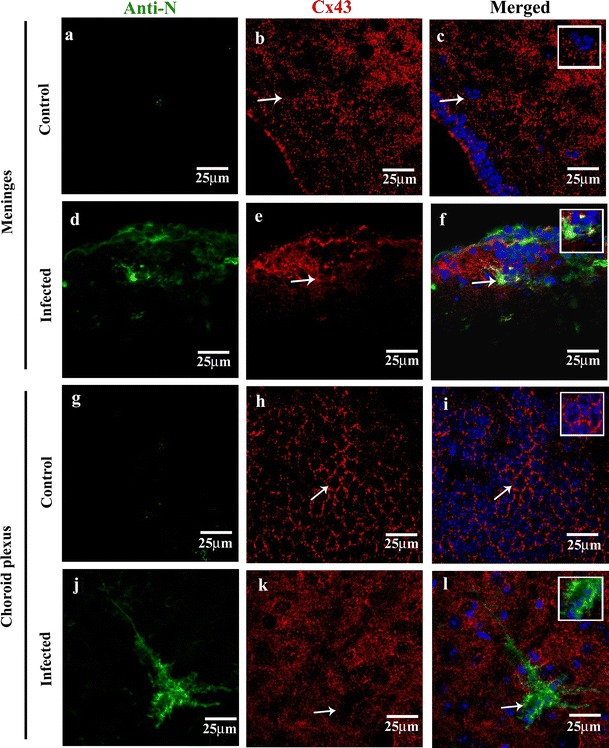
Reduced Cx43 punctate staining in MHV-A59-infected brain cryosections compared to mock-infected control mice brain section (a–f). Confocal images of 10-μm brain cryosections from the cortical meningeal region of mock-infected control (a–c) and MHV-A59-infected (d–f) brain sections double-immunolabeled with anti-viral nucleocapsid (N, green) and anti-Cx43 (red) showing reduced Cx43 punctate staining. Control sections (b, c) displaying a characteristic punctate Cx43 staining (b, c: arrow and inset), while the infected brains (e, f) exhibiting diffused Cx43. Merged image (f: arrow) showing an infected cell with internalized Cx43 staining in perinuclear region; inset showing an enlarged view of the infected cell. (g–l) Confocal images of 10-μm thin brain cryosections from the choroid plexus region of mock-infected control (g–i) and MHV-A59-infected (j–l) brain sections double-immunolabeled with anti-viral nucleocapsid (N, green) and anti-Cx43 (red) showing reduced Cx43 punctate staining. Control sections showing a characteristic punctate Cx43 honeycomb like pattern (h, i: arrow and inset), which appear as diffused staining in infected brains (k, l). Merged image (l: arrow) showing infected cells with reduced Cx43 punctate staining; inset showing an enlarged view of the infected cell. No anti-viral N staining was noted in the control brain sections (a–c, g–i). All sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to visualize nuclear localisation
