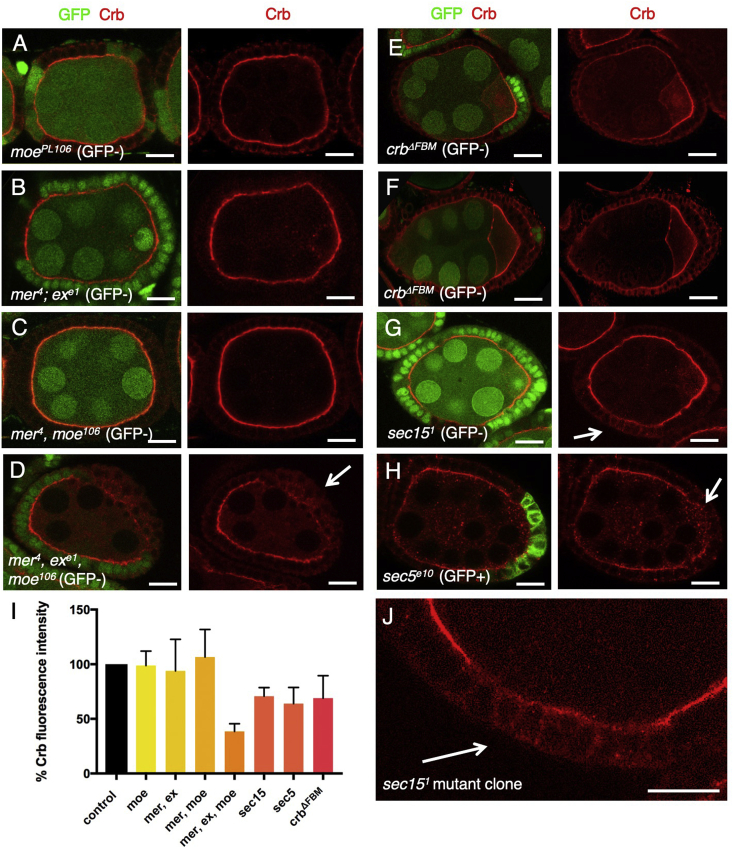
Fig. 5.
Apical FERM domain proteins and the Exocyst promote apical localisation of Crb.
A) Mutant clones for moesin, marked by absence of GFP, show normal Crb localization (n > 12 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
B) Double mutant clones for merlin and expanded, marked by absence of GFP, show normal Crb localization (n > 6 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
C) Double mutant clones for merlin and moesin, marked by absence of GFP, show normal Crb localization (n > 14 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
D) Triple mutant clones for merlin, expanded and moesin, marked by absence of GFP, show loss of apical Crb localization (n > 4 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
E) Mutant clones for crbΔFBM, marked by absence of GFP, showing weakly reduced apical Crb localization (n > 3 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
F) Mutant clones for crbΔFBM, marked by absence of GFP, showing strongly reduced apical Crb localization (n > 6 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
G) Mutant clones for sec15, marked by absence of GFP, show loss of apical Crb localization (n > 5 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
H) Mutant clones for sec15, marked positively by expression of GFP, show loss of apical Crb localization in extruded cells (n > 7 stage 6–9 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
I) Quantification of average apical Crb fluorescence pixel intensity, measured with Image J in n > 20 cells per genotype.
J) Zoom image of (G) showing mislocalisation of Crb in sec151 mutant cells.