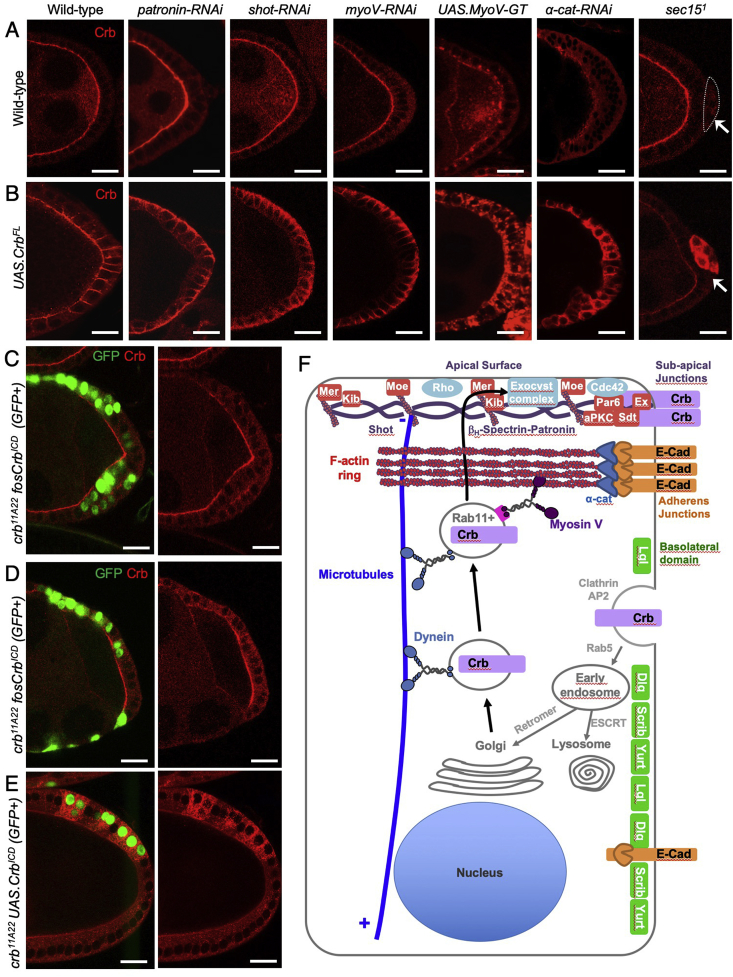
Fig. 6.
Overexpression of Crumbs is a sensitized assay to identify genes required for its apical trafficking and delivery.
A) Crb localization in wild-type posterior follicle cells and those of the indicated genotypes, either transgenes expressed with tj.gal4 or mutant clones of sec15 (arrow) (n > 8 samples per experimental condition; posterior region of stage 7/8 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
B) Overexpressed full-length Crb localization in otherwise wild-type posterior follicle cells and those of the indicated genotypes, either transgenes expressed with tj.gal4 or mutant clones of sec15 (arrow). Note the strong accumulation of overexpressed Crb upon manipulation of key trafficking regulators, including those that disrupt the microtubule cytoskeleton. Thus, although some factors are normally dispensable for endogenous Crb localization, they are essential to localise overexpressed Crb (n > 8 samples per experimental condition; posterior region of stage 7/8 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
C) Null mutant clones for crb expressing Crb intracellular domain (ICD) at endogenous levels from a fosmid (marked by expression of GFP; posterior region of stage 7/8 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
D) Null mutant clones for crb expressing Crb intracellular domain (ICD) at endogenous levels from a fosmid (marked by expression of GFP; posterior region of stage 7/8 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
E) Null mutant MARCM clones for crb expressing Crb intracellular domain (ICD) at high levels with the GAL4/UAS system (marked by expression of GFP; posterior region of stage 7/8 egg chambers; scale bar approximately 10 μm).
F) Schematic diagram of key components of the cellular cytoskeleton and trafficking machinery and their functions in localising Crb to the apical domain of epithelial cells.