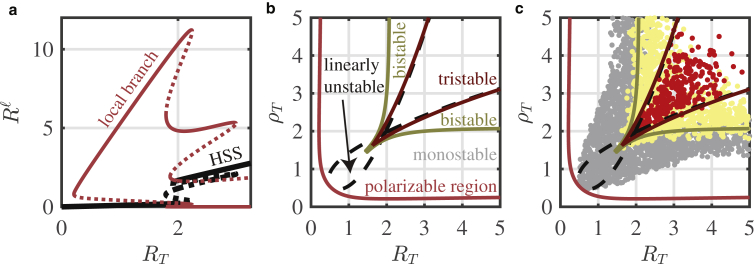
Figure 7.
LPA bifurcation diagrams confirms parameter space structure. (a) The Rac global (black) and local (red) solution branches are plotted with their stability (stable → solid; unstable → dashed) with respect to RT. (a) The tristable regime sits within a region of polarizability. As in Fig. 3a, perturbations across thresholds (dashed red lines) may induce polarization as the local perturbation grows to a value (solid red lines) that differs from the background HSS (black curve). (b) Two-parameter bifurcation diagram of (a) with respect to ρT is shown. The region of tristability sits within a larger region of bistability, which sits within a larger region of polarizability. The red curve is a continuation of the fold bifurcation with the lowest RT of the local solution branch from (a). The dark red and dark yellow curves are fold continuations from the well-mixed branch. The black dashed curves are the continuation of Turing bifurcations (the branch points where the local solution branches bifurcate from the global HSS solution branch). See Methods for further details of the bifurcation analysis. (c) A slice of the 5D parameter space from the PDE screen (Fig. 5, d–f) is plotted in the (RT, ρT) plane. To match the parameters used to produce the bifurcation diagram in (a) and (b), only polarizable parameter sets with 1.3 < a < 2.3, 3.5 < b < 4.5, and 0 < c < 0.025 from the PDE screen are plotted. Red points: tristable and polarizable parameter sets. Yellow points: bistable and polarizable. Gray points: monostable and polarizable. Parameters used are listed in Numerical Bifurcation Analysis. To see this figure in color, go online.