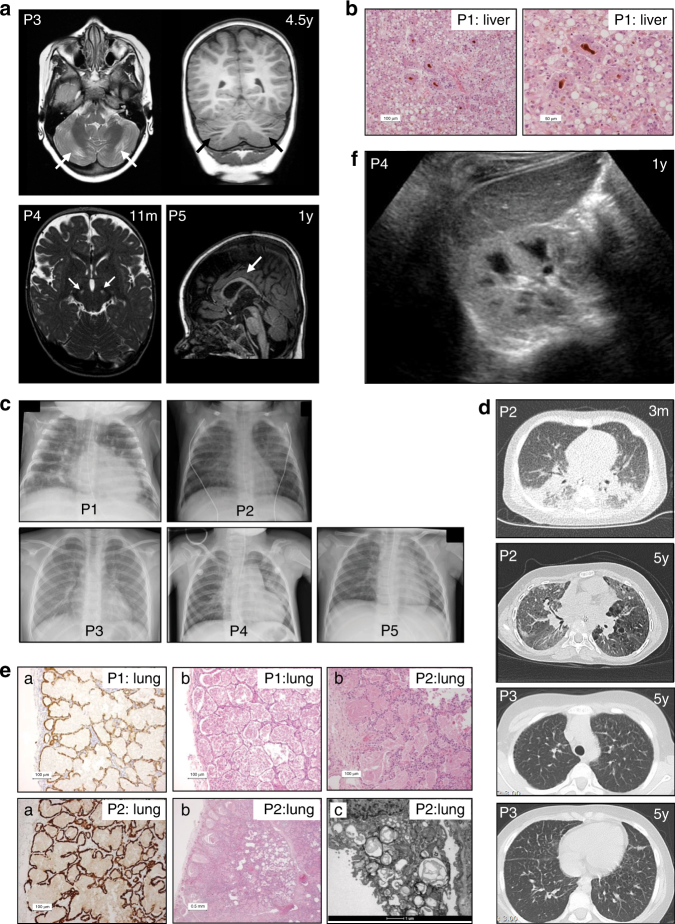
Fig. 3. Radiologic and histologic findings.
(a) Brain magnetic resonance image (MRI) scans of P3, P4, and P5. T2-weighted axial and T1-weighted coronal MRI in P3 at age 4.5 years show focal atrophy of the cerebellar cortex. T2-weighted MRI in P4 at age 11 months shows abnormalities in the substantia nigra. T1-weighted MRI in P5 at age 1 year shows delayed myelination with a relatively thin corpus callosum. (b) Histology shows severe cholestasis and steatosis in liver tissue (P1) in H&E staining (pseudorosette formation around bile plugs (brown). (c) Chest X-rays of P1–5. Interstitial abnormalities are visible in P1–P4. (d) Thoracic computed tomography (CT) scan in P2 at age 3 months shows extensive bilateral peribronchial consolidations, bronchus dilation, and subpleural ground glass consolidation with a remarkable dorso-basal distribution; at age 5 years it shows diffuse ground glass abnormalities, cystic lesions in a paraseptal–subpleural–bronchovascular distribution, and some thickening of interlobular septae. Thoracic CT scan in P3 at age 5 years shows thickening of interlobular septae in the upper and lower thorax. (e) Histology shows severe pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in lung tissue (P1 and P2) by staining for pankeratin marker CKAE1/3: (a: highlights the lining of the alveoli with reactive type 2 pneumocytes, b: H&E staining; b: P1 and P2 alveoli are filled with a dense, eosinophilic, amorphous, protein-lipid precipitate; P2 shows granular material in multivesicular bodies and absent formation of lamellar bodies in type 2 pneumocytes, and c: electron microscopy; c: alveoli contain laminated annular structures [lamellar bodies]). (f) Ultrasound of the kidneys in P4 shows a hyperechogenic cortex of the kidneys. The global intensity of the kidney cortex versus medulla and liver is too intense