Figure 6. Inhibition of peptides derived from the HR1 and HR2 regions in S2 subunit of MERS-CoV S protein on MERS-CoV infection.
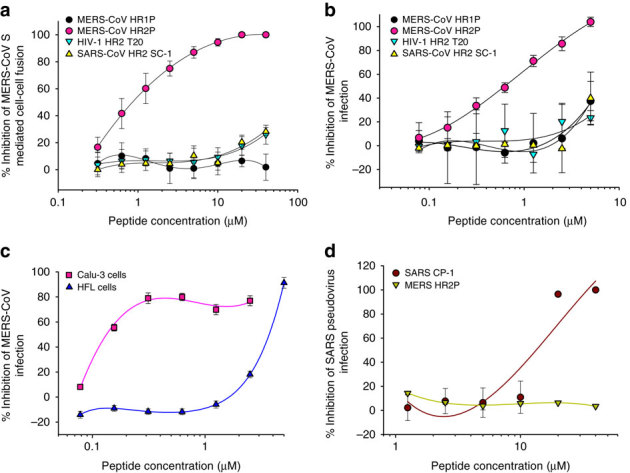
(a) Inhibitory activity of HP1P and HR2P peptides on MERS-CoV S protein-mediated cell–cell fusion. The HIV-1 HR2-peptide T20 was used as a control. The number of 293T/MERS/EGFP cells fused or unfused with Huh-7 cells were counted under an inverted fluorescence microscope, and the percentage of inhibition was calculated as described in the Methods. (b) Inhibitory activity of HP1P and HR2P peptides on MERS-CoV replication. The HIV-1 HR2-peptide T20 and SARS-CoV HR2 peptide SC-1 were used as controls. (c) Inhibitory activity of HR2P peptide on MERS-CoV replication in Calu-3 and HFL cells. The HIV-1 HR2-peptide T20 and SARS-CoV HR2 peptide SC-1 were used as controls. (d) Inhibitory activity of MERS-CoV HR2 peptide HR2P and SARS-CoV HR2 peptide SC-1 on SARS-CoV infection. The HIV-1 HR2-peptide T20 was used as the control. The cytopathic effect caused by MERS-CoV replication was assessed with MTT assay (b and c), while the SARS-CoV pseudovirus infection in 293T/ACE2 cells was detected by luciferase assay (d). The percentage of inhibition was calculated as described in the Methods. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data are expressed as means±s.d. (error bar). The experiment was repeated twice, and similar results were obtained.
