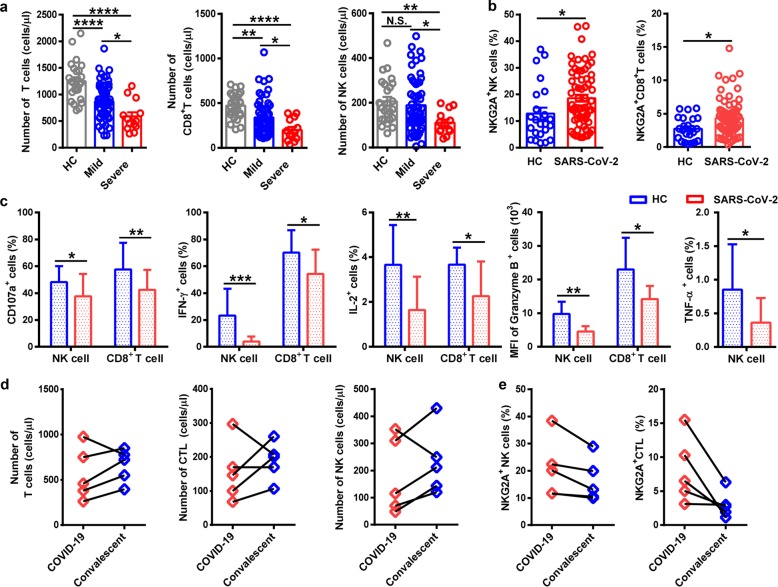
Fig. 1.
NKG2A+ cytotoxic lymphocytes are functionally exhausted in COVID-19 patients. a Absolute number of T cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells in the peripheral blood of healthy controls (n = 25) and patients with mild (n = 55) and severe (n = 13) infection with SARS-CoV-2. b Percentages of NKG2A+ NK cells and NKG2A+CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood of healthy controls (n = 25) and patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (n = 68). c Expression of intracellular CD107a, IFN-γ, IL-2, and granzyme-B in gated NK cells and CD8+ T cells and percentage of TNF-α+ NK cells in the peripheral blood of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and healthy controls. d Total number of T cells, CTLs, and NK cells in the peripheral blood of COVID-19 patients and convalescing patients. e Percentages of NKG2A+ NK cells and NKG2A+ CTL in the peripheral blood of COVID-19 patients and convalescing patients. Data are mean ± SEM. Unpaired/paired two-tailed Student’s t tests were conducted. p < 0.05 was considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; N.S., not significant