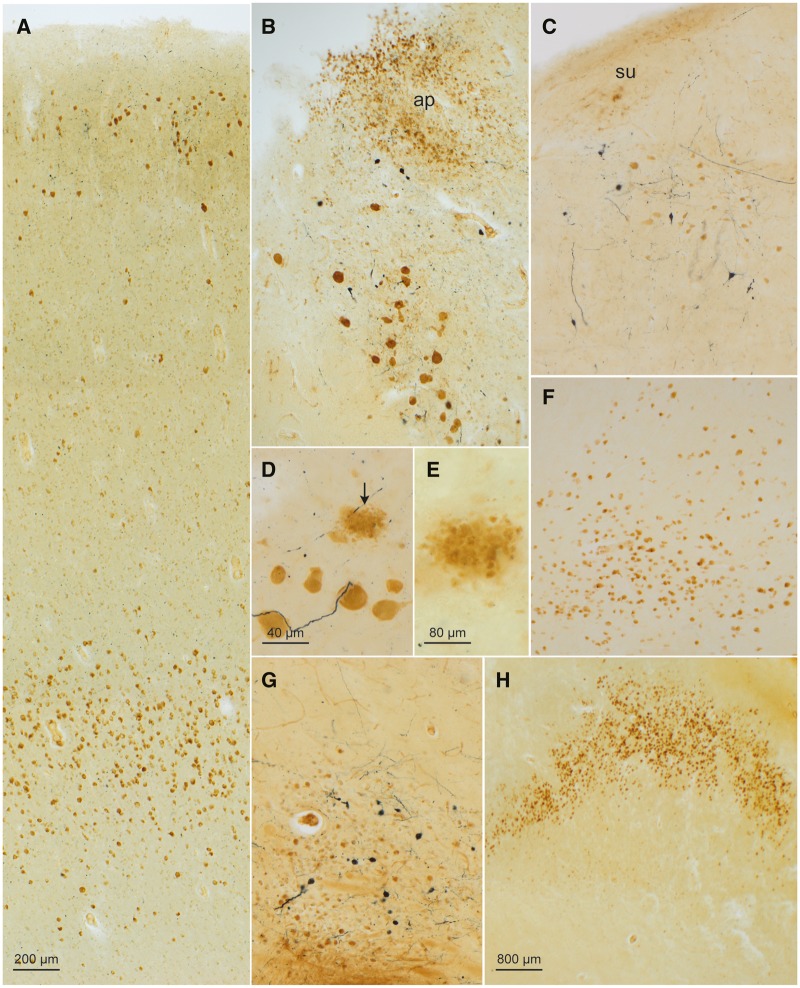
FIGURE 1.
CD77-immunopositive intraneuronal inclusions in a 58-year-old male with Fabry disease. (A) Gb3 accumulations (DAB, brown chromogen) occurred chiefly in nerve cells of the superficial cellular layers (II and IIIa) and deep layer (V) of the prepiriform cortex (Brodmann Area 51). The afferents to this area originate in the olfactory bulb, retrobulbar region, olfactory tubercle, septal region, amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex, and contralateral piriform cortex. The connectivity of the piriform cortex indicates its role as a link between the olfactory and limbic system. Also detectable in this micrograph, upon closer inspection, in the upper and lower cellular layers is syn-1-immunopositive Lewy pathology (SK-4700, dark blue chromogen). (B) Gb3 inclusions in nerve cells of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagal nerve and in astrocytes of the area postrema (ap) of the glossopharygeus-vagus nuclear complex. In addition, Lewy pathology (LP) was present in the somata and cellular processes of nerve cells in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagal nerve (SK-4700). (C) The prepositus hypoglossal nucleus also displayed Gb3 inclusions (DAB) and LP (SK-4700). A few nerve cells in the subventricular nucleus (su) were also CD77-positive. (D) Gb3 accumulation in motoneurons (DAB) of the motor nucleus of the facial nucleus accompanied by Lewy neurites (dark blue chromogen) and extraneuronal remnants of Gb3 (arrow) marking cell loss (E) there. (F) CD77 immunoreactivity (DAB) in nerve cells of the cortical accessory nucleus of the amgydala. (G) Gb3 inclusions (DAB) in nerve cells of the cholinergic nucleus of the diagonal band (similar pathology was also present in the basal nucleus of Meynert and bed nucleus of the terminal stria of the same case). (H) Severe intraneuronal Gb3 pathology in the prosubiculum. Immunonegative portions below the wave-shaped prosubiculum belong to pyramidal layers of the subiculum. Immunoreactions: CD77 (DAB, brown chromogen) or CD77 (DAB) plus syn-1 (SK-4700, dark blue chromogen) in 100 µm sections. Scale bar in (A) applies to (B), (C), (F), and (G).