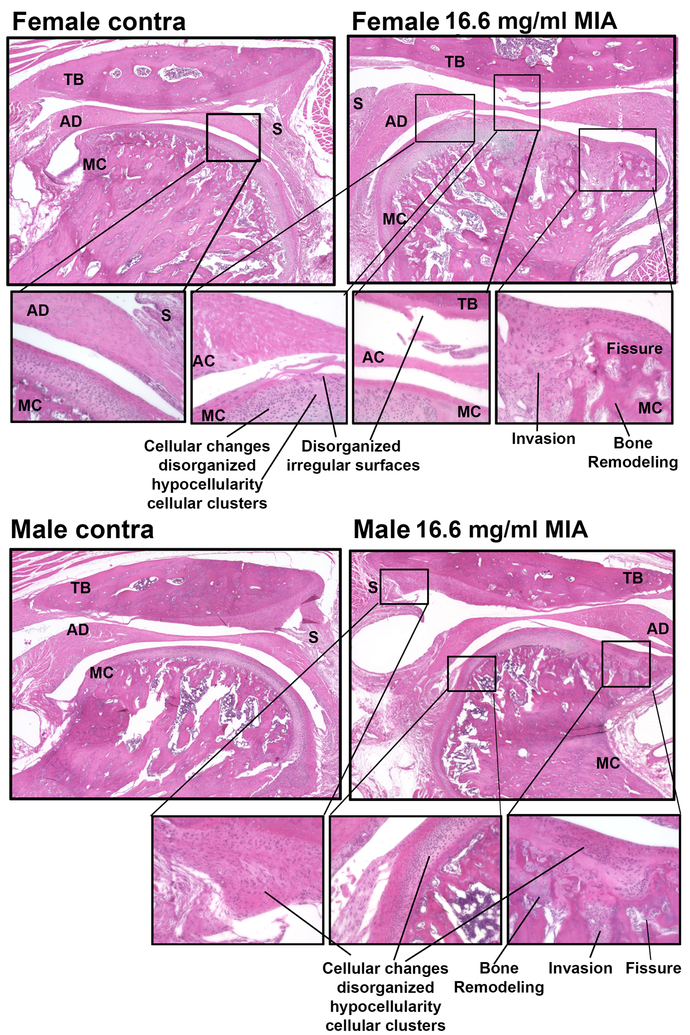
Figure 2.
H&E demonstrates low-dose MIA induced similar levels of pathology of the TMJ joint in female and male rats. The contralateral TMJ demonstrates normal structure of the temporal bone, articular disc (meniscus), synovium, and mandibular condyle which has normal cellular organization in the surface of the condyle. In MIA treated TMJ, there is clear loss of regular alignment and multilayer arrangement of chondrocytes in the mandibular condyle and the temporal bone. The articular surface of both the temporal bone and mandibular condyle demonstrate disorganized irregular surfaces. Female and male rats treated with low dose MIA also demonstrate enlargement of the articular disk and bone remodeling in the mandibular condyle. TB-temporal bone, AD-articular disk, MC-mandibular condyle, S-synovium. Call out images taken with 20x objective.