TABLE 1.
Examples of visual and phonological neighbors in Arabic (Source: adapted from Asaad and Eviatar, 2014).
| Arabic script | IPA |
| Visual neighbors | |
 |
/b/ |
 |
/θ/ |
 |
/t/ |
 |
/j/ |
 |
/q/ |
 |
/f/ |
 |
/x/ |
 |
/ħ/ |
 |
|
 |
/r/ |
 |
/z/ |
| Phonological neighbors | |
 |
/tʔ/, /t/ |
 |
/dʔ/, /d/ |
 |
/s/, /sʔ/ |
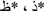 |
*/ð/, */ðʔ/ |
The phonemes marked with a (*) were not in the original paper by Asaad and Eviatar (2014) as they are not present in the Palestinian Arabic dialect. They do however, exist in both MSA and Emirati Arabic.
