Fig. 1.
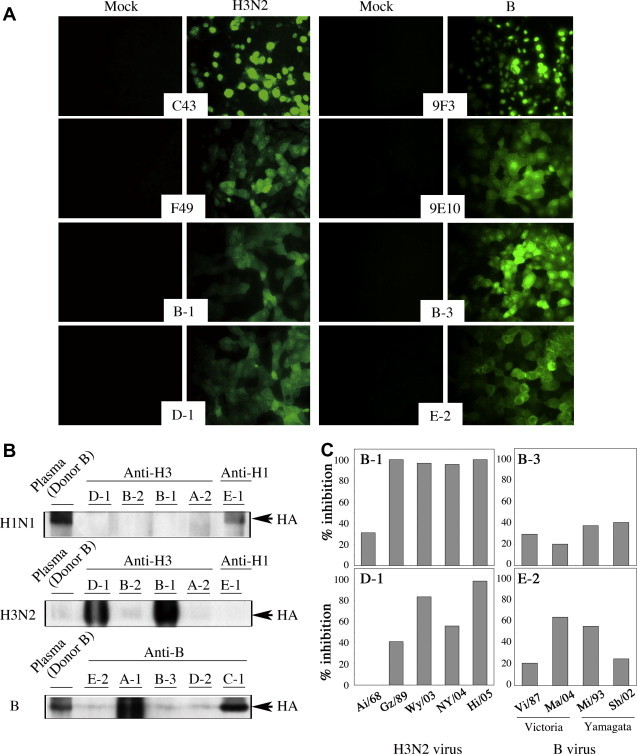
Broad reactivity of HuMAbs to influenza A and B viruses. (A) Specific immunostaining of influenza virus-infected MDCK cells was performed with HuMAbs B-1, D-1, B-3 and E-2. MDCK cells were mock-infected or infected with A/Hiroshima/52/05 (H3N2) and B/Malaysia/2506/04. As positive control, the following murine MAbs were used: C43 to NP and F49 to HA of H3N2; and 9F3 to NP and 9E10 to HA of B virus. (B) Viral protein recognized by HuMAbs was identified by Western blotting. The H1N1-, H3N2- and B-derived purified HA vaccine antigens were analyzed by SDS–PAGE, then immunoblotted with individual HuMAbs. As a positive control, a 2000-fold dilution of the plasma from vaccinated donor B was used. (C) Neutralizing activities of HuMAbs were evaluated with 100 FFU of influenza A H3N2 and B viruses. HuMAbs B-1 and D-1 for H3N2 and B-3 and E-2 for B, showing significant neutralizing activity against A/Hiroshima/52/05 (Hi/05; H3N2) and B/Malaysia/2506/04 (Ma/04; B), as shown in Table 2, were further examined for broad neutralizing activities against past vaccine strains: for H3N2, A/Aichi/2/68 (Ai/68), A/Guizhou/54/89 (Gz/89), A/Wyoming/2/03 (Wy/03), and A/New York/55/04 (NY/04); and for B, B/Victoria/2/87 (Vi/87), B/Mie/1/93 (Mi/93) and B/Shanghai/261/02 (Sh/02).
