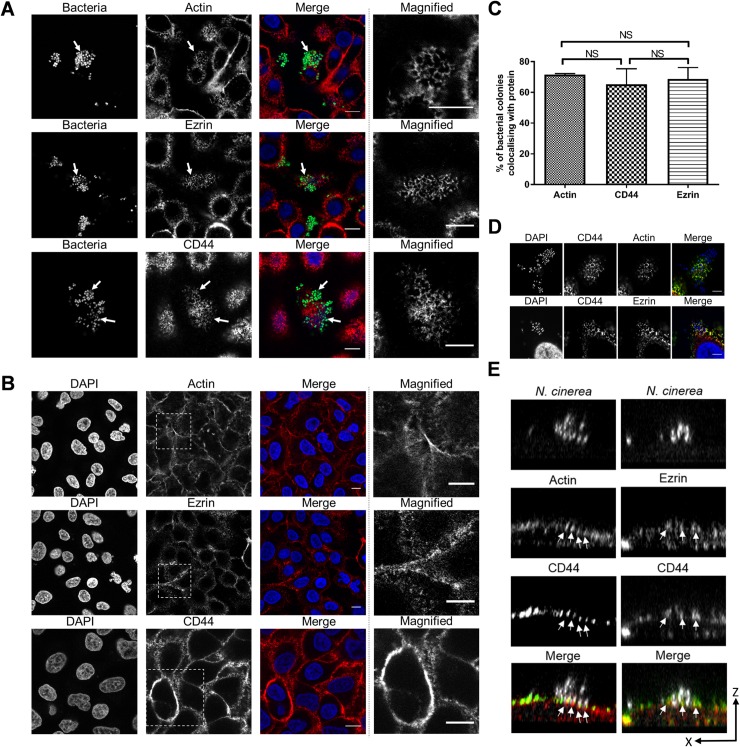
Fig 1. N. cinerea co-localises with components of cortical plaques on epithelial cells.
(A) Epithelial cells were infected for 3 h with N. cinerea expressing GFP and stained for CD44, ezrin or actin. Bacteria co-localised with each protein (white arrows); magnified areas in the panels on the right show the honeycomb-like arrangement of each protein. (B) Non-infected A549 cells were immunostained for CD44, ezrin or actin and analysed by microscopy. Magnified areas shown in the panels on the right do not show a honeycomb-like arrangement. Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Frequency of co-localisation of each protein in honeycomb-like arrangement at the site of attachment was determined by scoring 50 microcolonies. Data shown represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; NS, not significant. (D) Epithelial cells were infected for 3 h with N. cinerea and double fluorescence labelling was performed. Actin (red) and CD44 (green) in the top panels; or ezrin (red) and CD44 (green) in the bottom panels. Scale bars correspond to 10 μm. (E) XZ sections of cells dual labelled for actin (red) and CD44 (green), or CD44 (green) and ezrin (red). Bacteria and nuclei were stained with DAPI (white). Arrows indicate cellular protrusions enriched with actin-CD44 or ezrin-CD44.