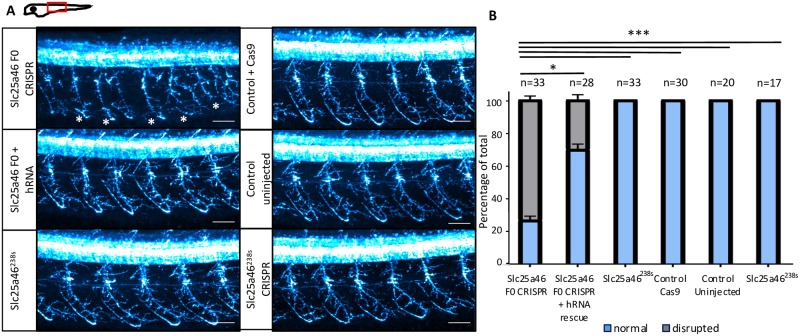
Fig 2.
CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of slc25a46 gene in zebrafish leads to significant motoneuron axon disruption in slc25a46 F0 but not in slc25a46238s zebrafish: (A) Confocal micrographs of 48 hpf zebrafish motoneurons stained with znp1 (cyan), whole mount, Z stack, lateral view captured above the yolk extension. Scale bar = 50 um. (B) Qualitative assessment of the primary motoneuron axon phenotypes: normal represent stereotypical “hook-like” axon path as in control images; disrupted–any number of abnormal motoneuron axons, such as axonal projections crossing into a nearby segment, truncated axons with projections not reaching back up to form the hook shape or aberrant hooks missing stereotypical branching pattern (indicated by white asterisks). P-values for comparisons between phenotypic penetrance in different genotypes are calculated by Fisher’s exact test (* for p<0.05; *** for p<0.001); n represents the number of individual larvae with observed motoneuron phenotype. Error bars represent SEM.