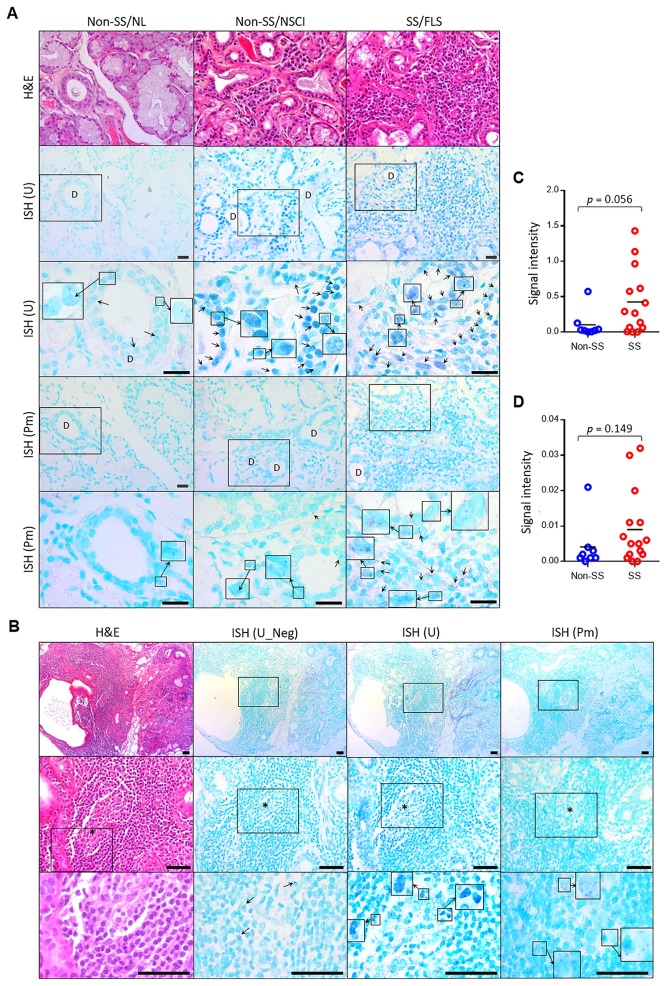
Fig 3. The presence of bacteria, including P. melaninogenica, within ductal cells and the infiltration areas of LSGs.
The sections of paraffin-embedded LSG tissues obtained from non-SS subjects or SS patients were subjected to H&E staining and in situ hybridization (ISH) using universal (U) or P. melaninogenica-specific (Pm) probes. As the negative control (Neg), sections were hybridized with a probe mixed with a 10-fold amount of unlabeled probe. (A) Representative areas of normal (NL) histology, nonspecific chronic inflammation (NSCI), and focal lymphocytic sialadenitis (FLS) are shown. Selected areas (square) were examined with higher magnification. Arrows indicate ISH signals in violet color and the shape of rod or cocci. D, duct. Scale bars indicate 25 μm. (B) A represented area of FLS with a germinal center (GC)-like structure is shown. The light zone is marked with *. Arrows indicate ISH signals in violet color with the shapes of rods or cocci. Several strong ISH signals were not completely inhibited in the negative control. Scale bars indicate 50 μm. (C and D) The signal intensities of ISH performed using the universal (C) or Pm-specific (D) probes were measured.