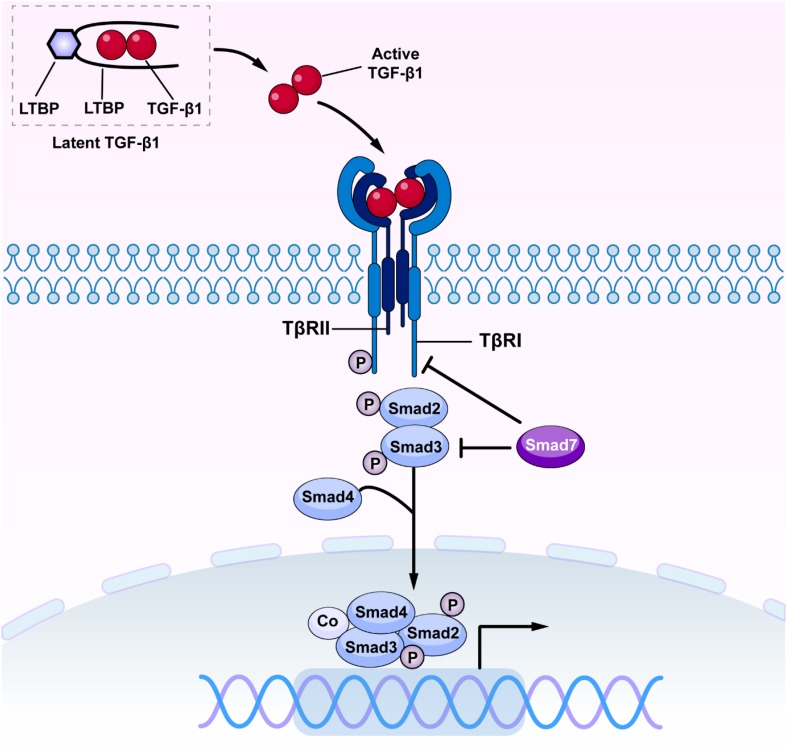
FIGURE 1.
The canonical TGF-β/Smad signaling in fibrosis. Once released, active TGF-β1 binds TβRII and activates TβRI and R-Smads (Smad2 and Smad3), resulting in formation of a complex with Smad4. The Smad2/3/4 complex then translates into the nucleus and binds to the target genes to induce fibrosis and inflammation. TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TβRI, TGF-β receptor type I; TβRII, TGF-β receptor type II.