FIG 8.
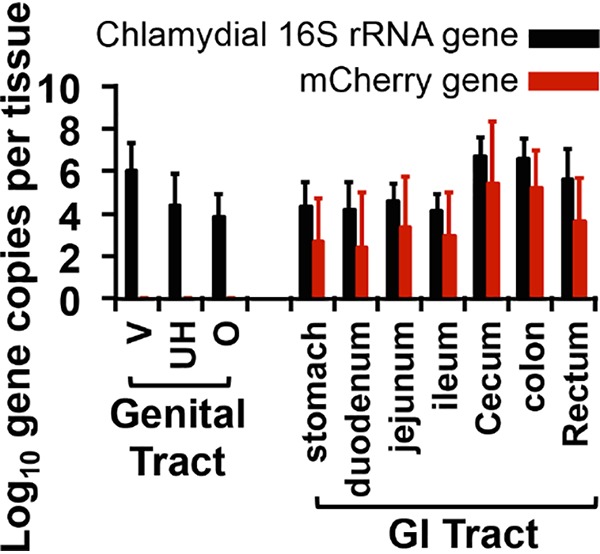
Monitoring chlamydial genomes from mice coinoculated with both plasmid-free and wild-type chlamydial organisms. Tissue samples from the same CBA/J mice (n = 5) intravaginally inoculated with Pf C. muridarum and intragastrically coinoculated with wild-type (red) Chlamydia 7 days after intravaginal inoculation as described in the Fig. 7 legend were also used for detecting chlamydial DNA using qPCR. The results are expressed as the log10 chlamydial 16S rRNA (black bars) or mCherry (red bars) gene copy numbers, as shown along the y axis. Genital tissues include vagina/cervix (V), uterine horn (UH), and oviduct and ovary (O), while GI tissues include stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, colon, and rectum tissues, as listed along the x axis.
