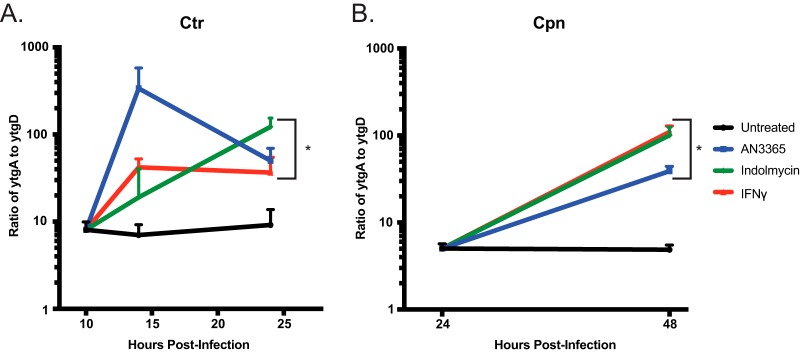
FIG 8.
Transcriptional analysis shows a decrease in read-through efficiency of the ytgABCD operon during 120 μM indolmycin, 1 μg·ml−1 AN3365, or IFN-γ treatment in C. trachomatis (Ctr) (A) or C. pneumoniae (Cpn) (B). RT-qPCR was performed to determine nanograms of cDNA of both ytgA and ytgD. Each was normalized to genomic DNA (gDNA) collected from replicate wells and expressed as a ratio of nanograms cDNA per nanograms gDNA of ytgA over ytgD. Student's t test was used to compare each 24 hpi value to that at 10 hpi untreated in C. trachomatis and each 48 hpi value to that at 24 hpi untreated in C. pneumoniae following Log10 transformation. *, P < 0.05.