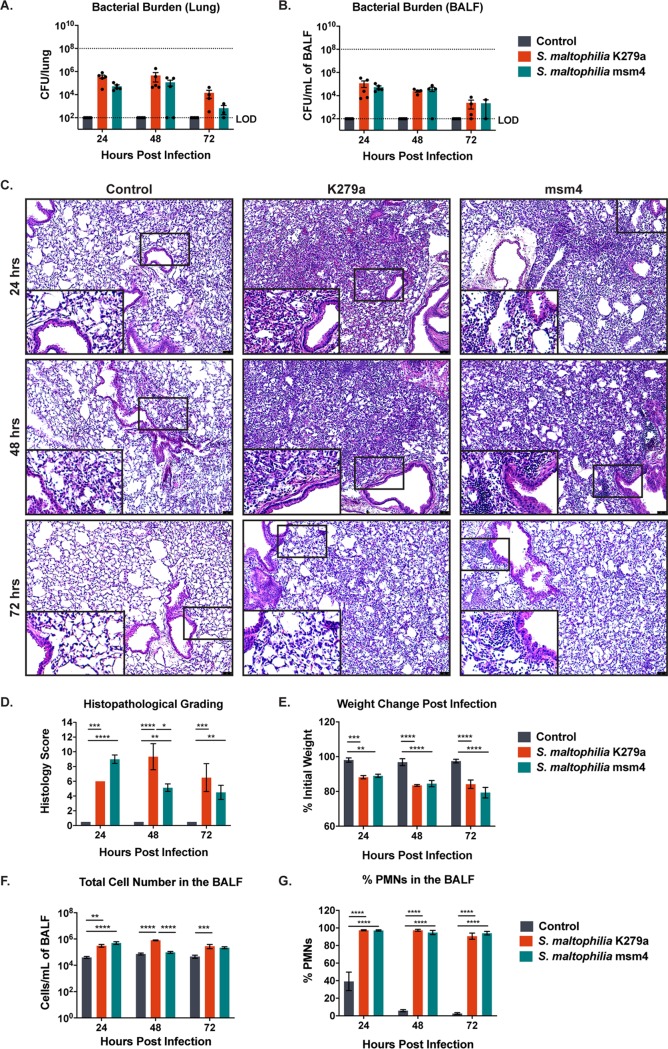
FIG 1.
S. maltophilia persists in the lungs of BALB/cJ mice with pathological consequences. BALB/cJ mice were intratracheally infected with ∼108 CFU of S. maltophilia K279a or S. maltophilia msm4, and groups were euthanized at 24, 48, and 72 hours postinfection. Bacterial counts in the lung homogenate (A) or in the BALF (B) were enumerated via viable colony counting. (C) Representative images of H&E-stained lung sections from infected and control animals were taken. (D) Severity of infection as indicated by H&E-stained sections were examined and graded in blind fashion by a board-certified veterinary pathologist (T.S.) for a semiquantitative histology score. (E) Weight loss was monitored postinfection. Total immune cell number (G) and percentage of PMNs (F) and in the BALF were quantified by differential cell counts. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 to 6. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc comparisons, *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Significant outliers were identified via ROUT method and removed. Groups with undetectable colony counts were represented at the limit of detection.