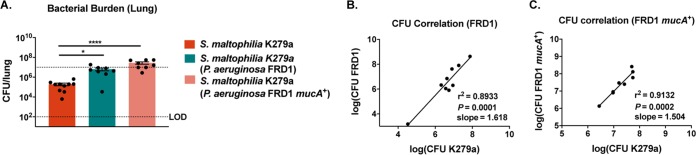
FIG 8.
The benefit conferred to S. maltophilia by P. aeruginosa is not alginate dependent. BALB/cJ mice were intratracheally infected with ∼107 CFU of S. maltophilia K279a and P. aeruginosa FRD1 or a nonmucoid isogenic mutant, P. aeruginosa FRD1/mucA+, at 24 hours postinfection. (A) Bacterial burden in the lung homogenate was enumerated via viable colony counting on differential medium. Mean ± SEM, n = 8 to 10. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc comparisons; *, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001. Significant outliers were identified via ROUT method and removed. Correlation between bacterial burdens of S. maltophilia K279a and P. aeruginosa FRD1 (B) and P. aeruginosa FRD1/mucA+ (C) was calculated; n = 8 to 9. Linear regression with automatic outlier elimination and two-tailed Spearman correlation were performed on log-transformed bacterial counts.