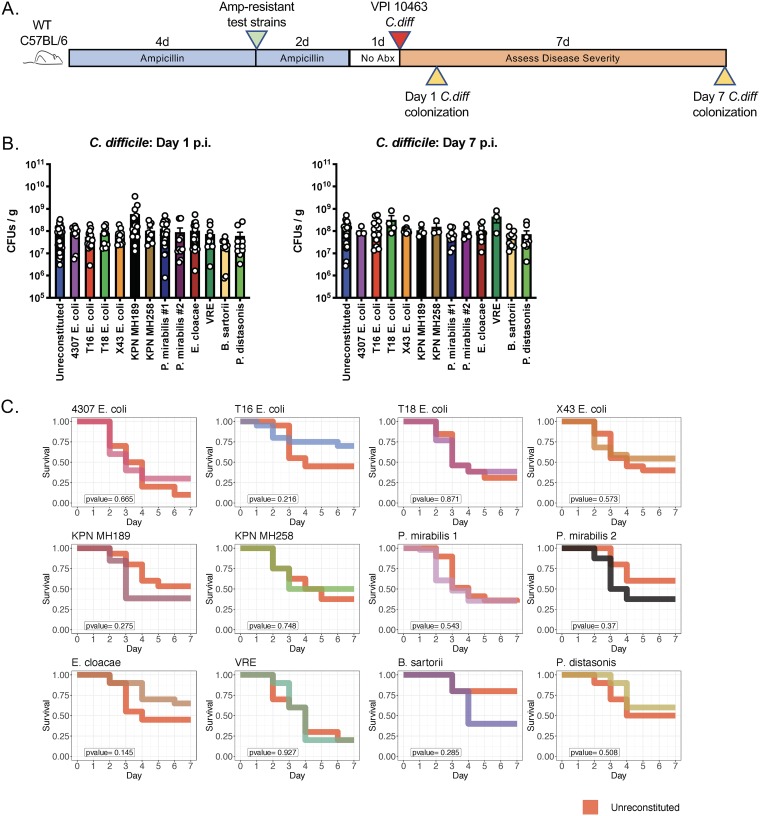
FIG 4.
The composition of the residual intestinal microbiota does not significantly influence survival following C. difficile infection. (A) Schematic of experimental design to determine the impact of residual microbiota composition on the outcome of C. difficile infection. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice (n, ≥10 per group; results from 17 independent experiments) were treated with ampicillin for 4 days and were then inoculated with 2 × 104 CFU of the antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains. Ampicillin was maintained in the drinking water for an additional 2 days. Mice were challenged with 200 C. difficile VPI 10463 spores via oral gavage 1 day after ampicillin withdrawal, and C. difficile colonization and mouse survival were monitored as indicated. (B) On day 1 and day 7 postinfection (p.i.), C. difficile CFU in fecal pellets were quantified using selective plating. (C) Survival was monitored for 1 week post-C. difficile infection.