Figure 7: Yck2 inhibition impairs the virulence of C. albicans in co-cultures and in mice.
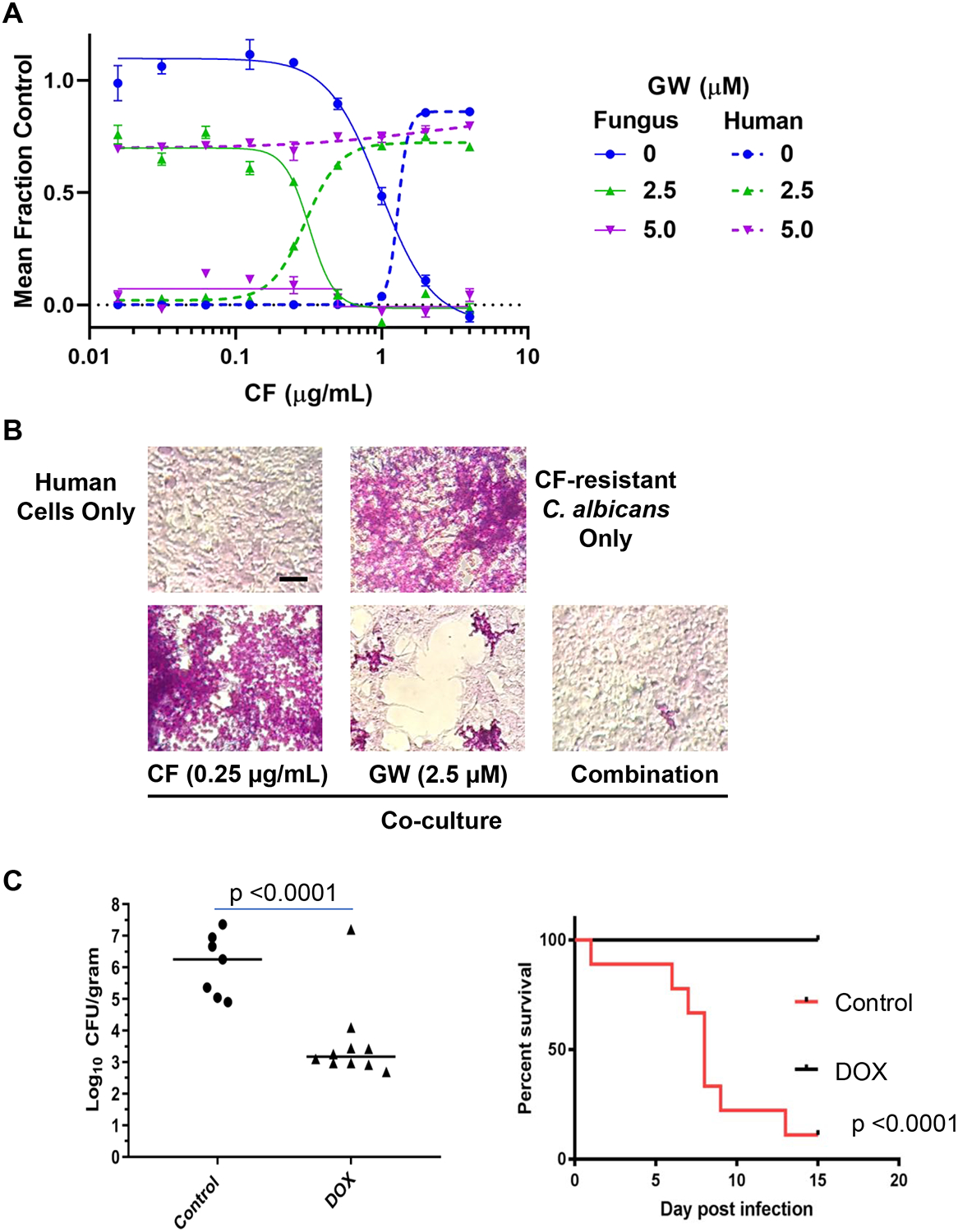
A, Relative growth/survival of human kidney-derived cells (293T) and CF-resistant C. albicans in co-culture. Concentration-dependent rescue of human cells by GW alone or in combination with CF is plotted in relationship to inhibition of fungal burden. Solid traces indicate relative number of GFP-marked CF-resistant fungi/well. Dashed traces indicate relative number of luciferase-marked human cells present in the same well. Each point depicts the mean of triplicate wells. Error bars, SEM. Four-parameter curve fitting was performed in Prism 7.0. The experiment was repeated once with quantitatively similar results. B, Representative photomicrographs of PAS-stained cultures after 3 days growth in standard cell culture medium under the indicated conditions are presented. Fungi appear as brightly stained pink yeast and hyphal forms upon background monolayers of light-colored human cells. Scale bar, 50 μM. C, Genetic-depletion of YCK2 significantly reduces virulence in mice. Left, Addition of DOX to chow of mice infected IV with DOX-regulated tetO-YCK2/yck2Δ C. albicans strain (106/mouse) markedly reduces kidney fungal burden 3 days after infection. Statistical significance of the difference between treatment groups was determined by Mann Whitney test (unpaired, 2 tailed, non-parametric). Addition of DOX to the chow of mice infected intravenously with caspofungin-resistant DOX-regulated tetO-YCK2/yck2Δ C. albicans strain (106/mouse) markedly improves survival. The statistical significance of differences between treatment groups was determined by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (9 mice per treatment group). (See also Figure S7).
