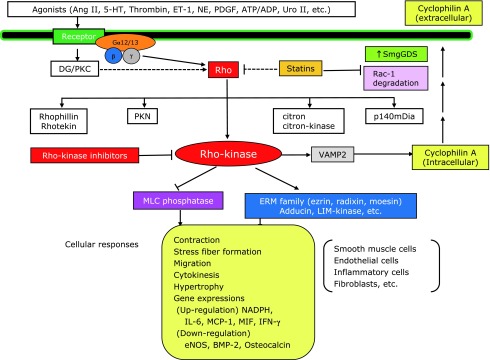
Fig. 4.
Role of Rho/Rho-kinase pathway in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Rho/Rho-kinase–mediated pathway plays an important role in the signal transduction initiated by many agonists, including angiotensin II (Ang II), serotonin (5-HT), thrombin, endothelin-1 (ET-1), norepinephrine (NE), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), adenosine triphosphate (ATP)/adenosine diphosphate (ADP), and urotensin II (Uro II). Through the modulation of its target effectors, Rho-kinase is substantially involved in vascular smooth muscle contraction (via inhibition of myosin phosphatase) and in the pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis (via activation of ERM, adducin, and other effectors). Whereas statins inhibit Rho at their relatively higher concentrations, they simultaneously inhibit pathways mediated by other G proteins, such as Ras and Rac. By contrast, Rho-kinase inhibitors selectively inhibit Rho-kinase pathway. Solid line indicates proven pathway and dashed line proposed pathway. DG, diacylglycerol; MLC, myosin light chain; PKC, protein kinase C; SmgGDS, small GTP-binding protein dissociation stimulator.