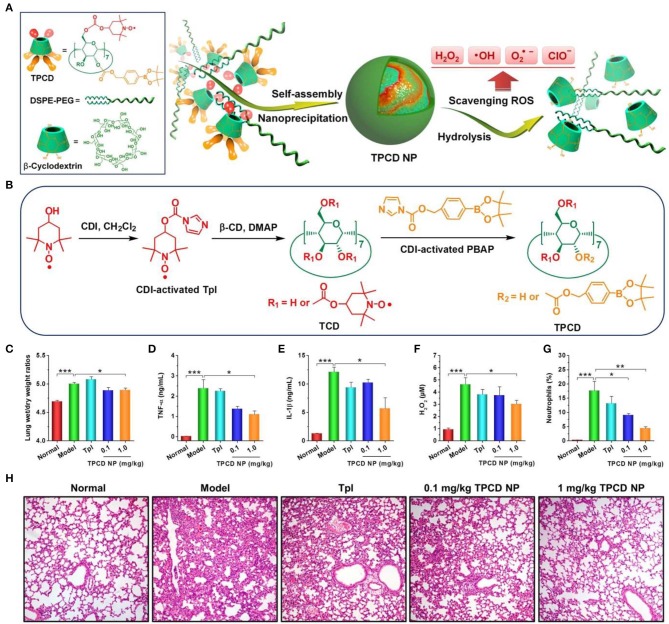
Figure 3.
Design and preparation broad-spectrum ROS-scavenging nanoparticles for treatment of acute lung injury (ALI). (A) Schematic illustration of engineering of a broad-spectrum ROS-scavenging material and its nanoparticles based on functionalized β-CD. (B) The synthetic route of β-CD conjugated with Tempol (Tpl) and PBAP units (TPCD). CDI, 1,1-carbonyldiimidazole; DMAP, 4-dimethylaminopyridine; TCD, Tpl-conjugated β-CD; PBAP, 4-(hydroxymethyl) phenylboronic acid pinacol ester. (C–H) Treatment of ALI with TPCD nanoparticles (i.e., TPCD NP) in mice. (C) The lung wet-to-dry weight ratios after different treatments. (D–G) The expression levels of TNF-α (D), IL-1β (E), and H2O2 (F) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from mice with LPS-induced ALI and subjected to different treatments. (G) Quantified neutrophil counts in pulmonary tissues of ALI mice. (H) H&E-stained pathological sections of lung tissues. Data are mean ± standard error (n = 6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Reproduced with permission from Li et al. (2018).