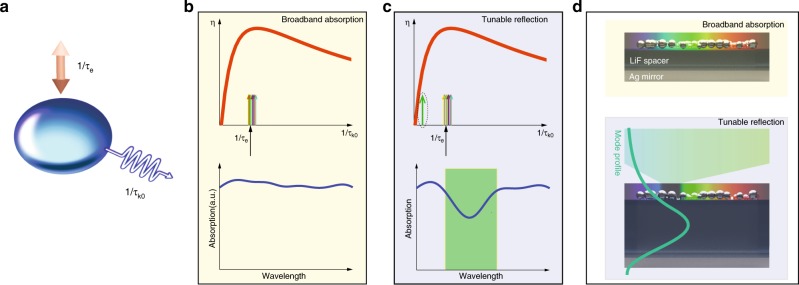
Fig. 1. A disordered system with transition from broadband absorption to band-limited reflection/transmission based on coupled mode theory.
a Schematic for a generalised optical cavity with coupling rate τe and intrinsic decay rate τk0 for the kth mode supported. b Broadband absorption regime. Upper panel: the disorder induces the convergence of intrinsic decay rates, leading to energy equipartition with similar coupling efficiency η for all the modes. Lower panel: broad absorption is achieved, computed with 25 modes with τk0 converging within [0.8, 1.2]τe. c Band-limited regime. Upper panel: sudden reduction of intrinsic loss of a specific mode; lower panel: an absorption dip is formed by enlarging the intrinsic decay τk0 (by 20) of specific mode. d A realistic design matching the CMT model, composed of a disordered plasmonic system on a cavity with plasmonic mirror beneath. The thickness t can tune the intrinsic decay rate of a specific mode, driving the system from a broadband absorption (upper panel, t is too small to hold a mode) to band-limited reflection (upper panel, with a mode confined around the plasmonic structures).