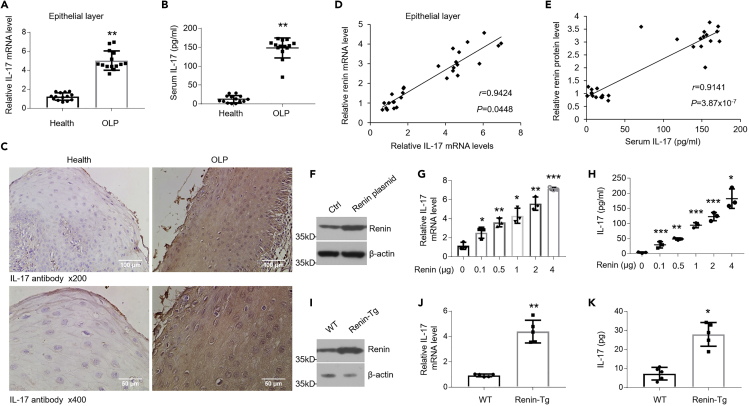
Figure 3.
Renin Upregulates IL-17 Expression in Oral Keratinocytes
(A) Real-time PCR quantification of IL-17 mRNA levels in oral keratinocytes from human specimens, n = 14.
(B) ELISA measurement of IL-17 concentrations in serum from healthy individuals or OLP patients, n = 14.
(C) IL-17 immunostaining in the oral tissues of healthy controls and OLP patients.
(D) Correlation of fold change between renin mRNA levels and IL-17 mRNA status in oral epitheliums of human biopsies.
(E) Correlation between renin protein levels in the human oral epithelial layer and IL-17 concentrations in serum of participants.
(F) Western blot analysis of renin protein levels in HOKs transfected with empty or renin plasmids, n = 3.
(G) Real-time PCR quantification of IL-17 mRNA levels in HOKs after renin transfection with different doses as shown, n = 3.
(H) ELISA detection of IL-17 productions in the culture medium of HOKs after renin transfection with different doses as shown, n = 3.
(I and J) Western blot (I) of renin expression or quantitative PCR test (J) of IL-17 mRNA levels in oral keratinocytes obtained from wild-type or renin-transgene mice, n = 5.
(K) ELISA examination of IL-17 expression in oral keratinocytes obtained from wild-type or renin-transgene mice, n = 5.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus corresponding control. Ctrl, control; WT, wild type. Data were shown as means ± SD. Two-tailed Student's t test was used.