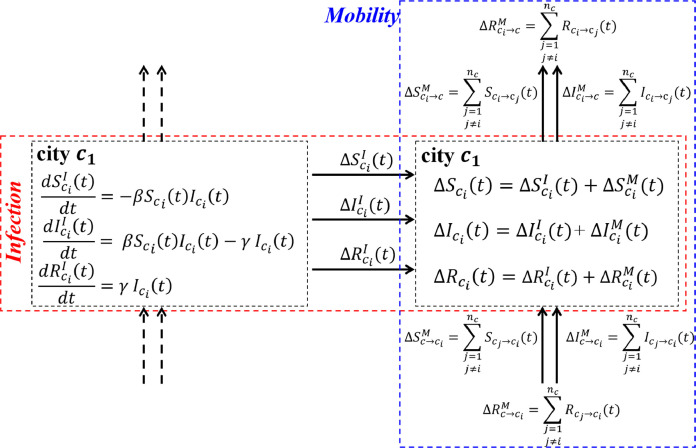
Fig. 1.
Multi-city travel SIR model.
*, and represent, respectively, the number of susceptible (S), infected (I) and recovered (R) people in city i at time t; β is the transmission rate; γ is the recovery rate; , and represent, respectively, the variations in S, I and R caused by infection in city i at time t; , and represent, respectively, the variations in S, I and R caused by human mobility at time t; nc is the total number of cities; , and represent, respectively, the S, I and R inflows from other cities to city i at time t; and , and represent, respectively, the S, I and R outflows from city i to other cities at time t.