Figure 2.
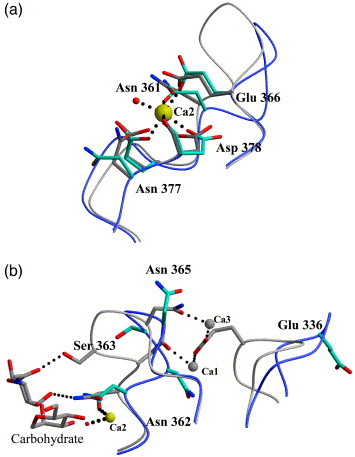
Carbohydrate-binding and calcium-binding sites. (a) Cα traces of the DC-SIGNR R8 (blue) and DC-SIGNR CRD (gray) primary calcium-binding sites showing side-chains involved in coordinating calcium. In the absence of carbohydrate, Asp377 is not involved in calcium coordination. The calcium ion, seen in nearly the same position in both structures is shown in yellow (Ca2). A water molecule (red) is present in the location where normally ligand binds (DC-SIGNR R8 structure). (b) The secondary calcium-binding site shows the Cα loop in DCSIGNR R8 and DC-SIGNR CRD Loop movement is observed between ligand-bound and apo structures from closed to open, respectively. Calcium ions present in the structure of DC-SIGNR CRD only are shown in gray (Ca1 and Ca3). Side-chain movements between each structure are summarized in Table 2.
