Figure 3.
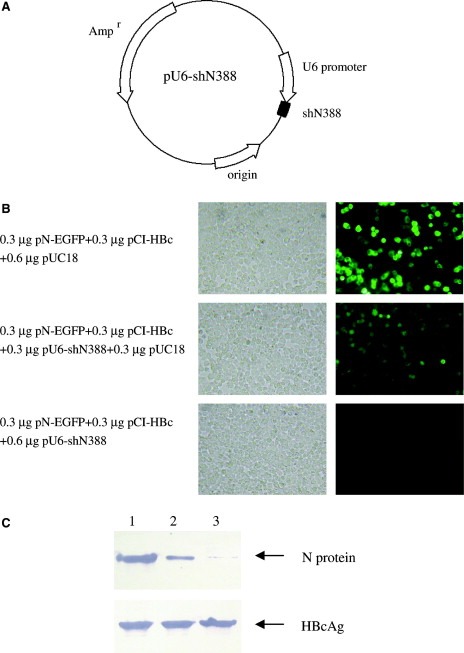
Inhibition of SARS‐CoV N protein expression by siRNA expression vector. The N388 siRNA expression vector was constructed and its influence on the N‐EGFP expression was detected in cultured 293T cells. (A) The PCR product of N388 siRNA expression cassette was inserted into the vector pMD‐18T, and the resulting plasmid was used as siRNA expression vector. (B) 293T cells were co‐transfected with plasmid pN‐EGFP and N388 siRNA expression vector, along with HBcAg expression plasmid as an unrelated control. The images show the EGFP expression at 48 h post‐transfection. The left panel shows the cells under a bright field. (C) The expression of N protein and HBcAg were detected by Western blot at 48 h post‐transfection. Lane 1: 293T cells transfected with 0.3 μg pN‐EGFP, 0.3 μg pCI‐HBc and 0.6 μg pUC18. Lane 2: 293T cells transfected with 0.3 μg pN‐EGFP, 0.3 μg pCI‐HBc and 0.3 μg pU6‐shN388. Lane 3: 293T cells transfected with 0.3 μg pN‐EGFP, 0.3 μg pCI‐HBc and 0.6 μg pU6‐shN388. In fluorescence and Western blot analysis, plasmid pUC18 was used to standardize the plasmid dosage for transfection. The experiment was repeated three times, and similar results were obtained.
