Fig. 2.
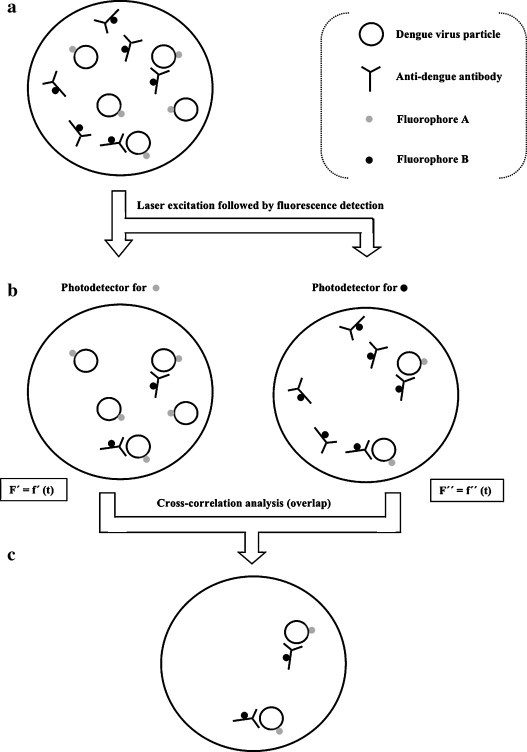
Principle of FCCS applied to the detection of specific interactions between dengue virus and an anti-dengue antibody. (a) Viral particles and antibodies are tagged with fluorophores of different colors and distinct fluorescence spectra (attachment of these dyes does not affect normal virus/antibody interactions). (b) The sample is irradiated at the excitation wavelengths of both dyes (with the same or different laser sources). The emission light beam is split and then two photodetectors (tuned for the emission wavelengths of each one of the dyes) monitor the sample simultaneously. Each photodetector detects both its corresponding particle-labeling dye and the interaction, by measuring fluorescence fluctuations with time. (c) Cross-correlation analysis between the two fluorescence spectra reveals solely the virus/antibody interactions. Cross-correlation analysis allows determining the amount and kinetic parameters of the interacting species.
