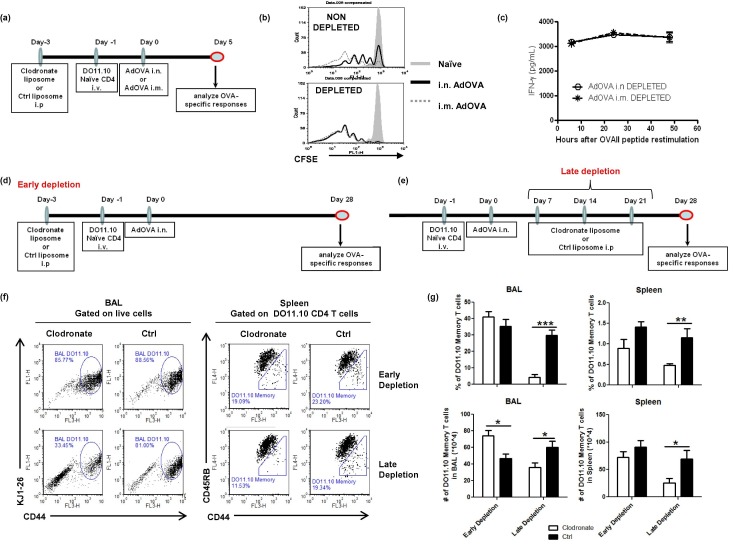
Fig. 7.
Macrophage depletion after immunization, but not prior to immunization, markedly reduces the number of tissue resident and systemic CD4 memory T cells. (a/d/e) Diagrams of macrophage depletion regimens used in the study. (b) Representative FACS plots showing CD4 T cell proliferation in the DLNs of i.n. immunized versus i.m. immunized mice with or without MΦ-depletion at day 3 post immunization. (c) IFN-γ recall responses in the splenocyte cultures of MΦ-depleted mice at day 5 post i.n or i.m. immunization. (f/g) DO11.10:BALB/c mice were treated with clodronate-containing liposomes or control liposomes at 3 days prior to AdOVA immunization or at 7, 18 and 24 days post immunization. CD4 memory T cells in BAL and spleen were determined by FACS at 4 weeks post immunization. The percentage and the number of DO11.10 CD4 memory T cells (CD44highCD45RBlow) are presented as the mean ± SEM of 5–8 mice per group pooled from two experiments. The differences between groups were analyzed using two-way ANOVA test (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).