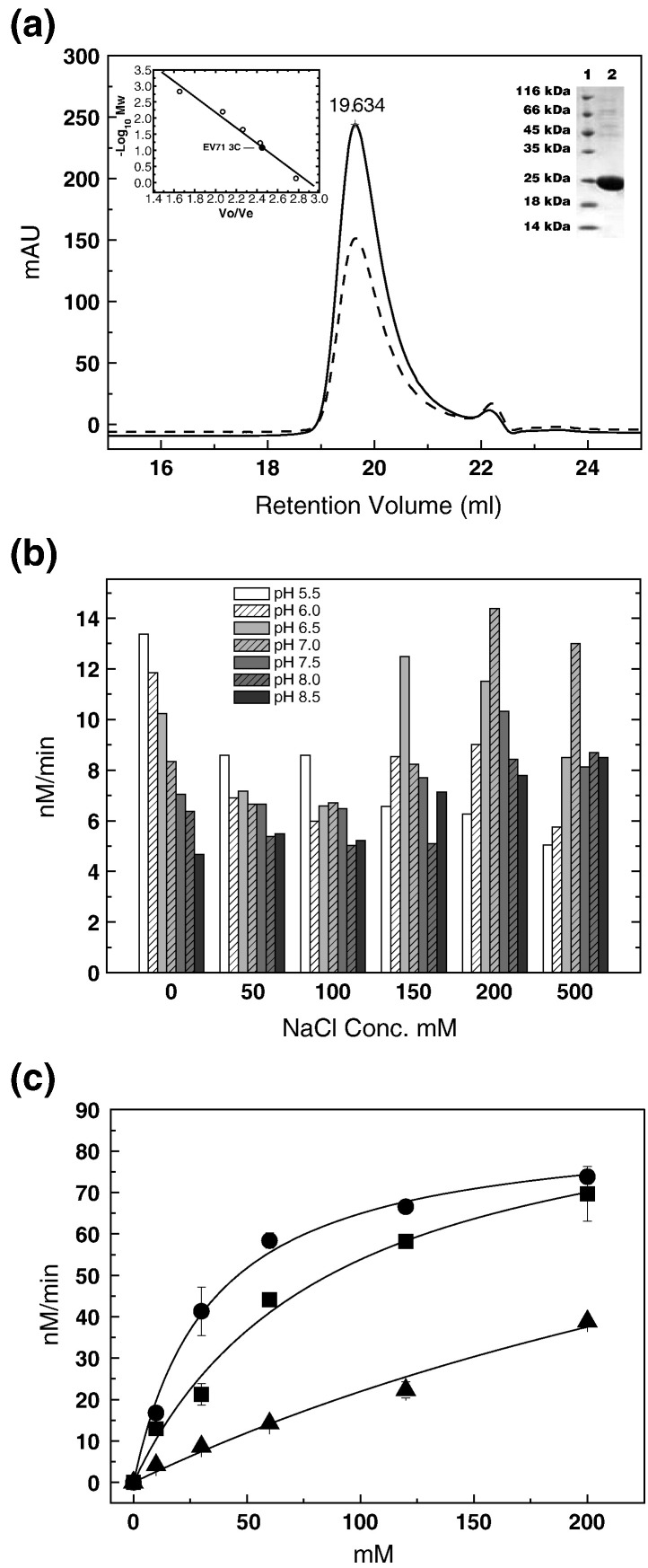
Fig. 3.
Biochemical characterization of EV71 3Cpro. (a) Size-exclusion chromatography and SDS-PAGE analysis of EV71 3Cpro protein. Chromatographic profiles are as follows: continuous line is UV absorbance at 280nm, and broken line is UV absorbance at 260nm. Upper-left inset: the − log (MW) values of standard proteins for size-exclusion column calibration (Superose 6 10/300GL) are plotted as the function of Ve/Vo (○). The data are fitted linearly to derive standard curve. The molecular mass of EV71 3Cpro is estimated at ∼ 17 kDa (●), indicating that EV71 3Cpro exists as monomer in solution. Upper-right inset: SDS-PAGE analysis of purified EV71 3Cpro. Lane 1, molecular mass standards; lane 2, EV71 3Cpro. (b) Optimization of protease assay conditions. The initial velocities of proteolytic reactions are measure in different reaction buffers with various combinations of salt (0–500 mM) and pH (pH 5.5–8.5). The best combination of salt and pH is determined as NaCl 200 mM (pH 7.0). (c) Substrate specificity of EV71 3Cpro. Fluorescence-quenching-pair-based proteolytic reactions are performed using different substrates: (●) substrate derived from the EV71 autoprocessing 3B–3C junction, (▪) substrate derived from the first cleavage site (251/252 aa) in CstF-64 and (▲) substrate derived from the autoprocessing site of a 3C-like protease in SARS-CoV. The concentration of the protease was 4 μM for all experiments.