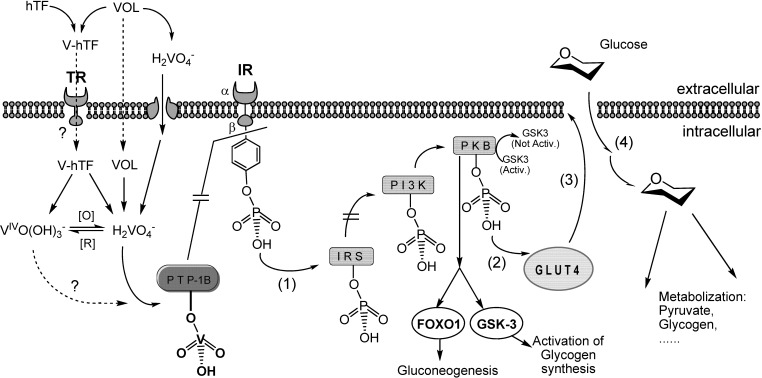
Fig. 8.
Simplified sketch of the possible mechanism of action of VCs. The internalization of glucose by the glucose transporter GLUT4, is triggered by the phosphorylated insulin receptor (IR). In the absence of insulin or insufficient insulin response, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP-1B) dephosphorylates the IR, and the glucose intake is stopped. By binding to PTP-1B vanadate may block PTP-1B, this restoring the signaling path. (1) Phosphate remaining bound to IRβ, the insulin receptor substrate (IRS), the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K, which activates protein kinase B, PKB, also known as Akt) remain phosphorilated, thus the signaling path is kept active and (2) activation of the glucose transporter remains in operation, as well as (3) translocation of GLUT4, and (4) cellular uptake of glucose by GLUT4.