Figure 1.
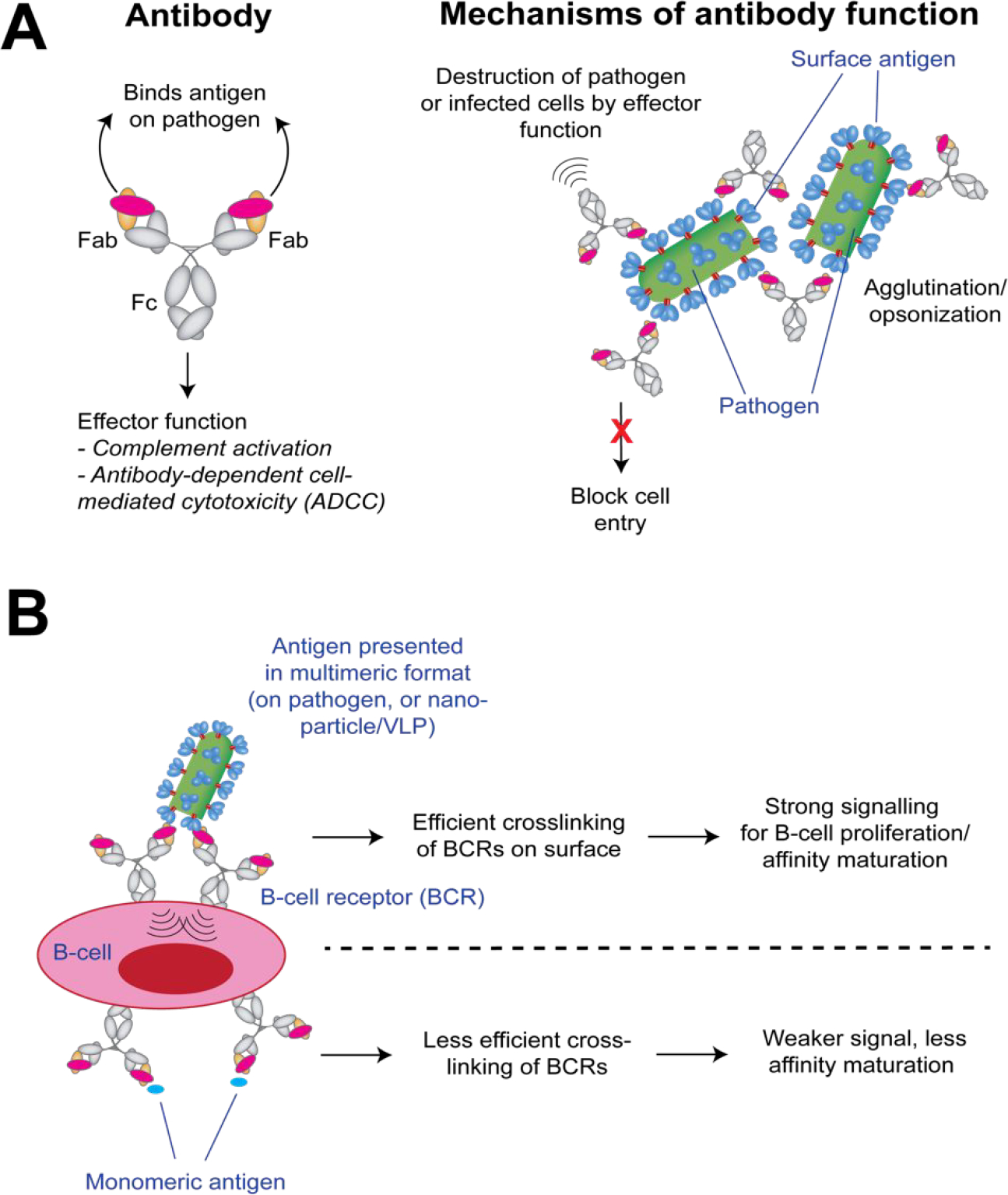
Antibody function and affinity maturation. (A) Mechanisms by which antibodies can protect against microbial pathogens. For the overall antibody architecture, the Fab region binds the antigen or pathogen, and the Fc region is responsible for effector function. (B) Affinity maturation requires cross-linking of B-cell receptors on the surface to signal survival and expansion of that clone. This cross-linking is more efficiently stimulated when antigens are presented in a multimeric format (e.g., on the pathogen, or on a nanoparticle or VLP).
