Figure 1.
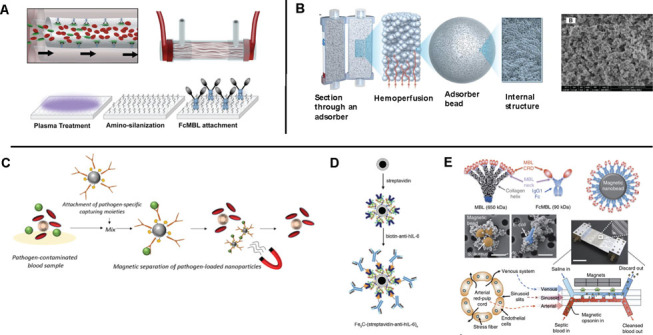
(A) A schematic drawing of surface adsorption-based extracorporeal devices. The inner surface of fibers bundled in the device is functionalized with proteins or synthetic polymers, which are known to capture a wide range of pathogens and toxins in blood18. (B) An illustration showing a cross-sectional view of porous beads and their internal structures of the CytoSorb® filter, which was developed for lowering cytokine levels in blood of septic patients20. (C, D, E) Magnetic particle-assisted blood treatment approaches. (C) Magnetic particles are functionalized with pathogen-capturing moieties21. (D) Magnetic particles coated with anti-IL6 was developed for removing a proinflammatory cytokine in blood22. (E) An engineered human FcMBL molecule conjugated on magnetic nanoparticles where the FcMBL molecules were designed to be oriented with carbohydrate recognition domains facing outward23.
