Figure 4.
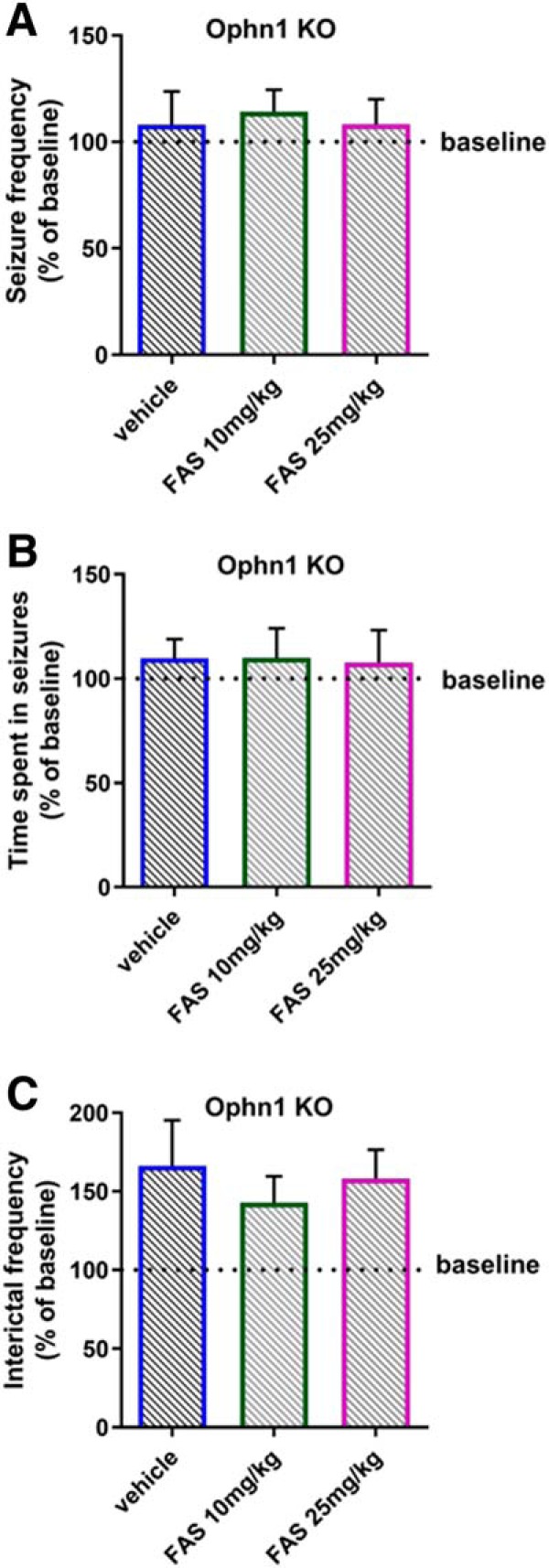
A single fasudil administration is not effective in rescuing the electrographic alterations in Ophn1 KO mice. Fasudil (FAS) was intraperitoneally administered in a group of KO mice (n = 7) at two different doses, 10 mg/kg and 25 mg/kg. Intraperitoneal injection of vehicle (saline solution) was used as control. No significant changes were found for the electrophysiological parameters: A, Number of seizures per 10 min of recording (two-way RM ANOVA, p = 0.203), B, Time spent in ictal activity per 10 min of recording (two-way RM ANOVA, p = 0.139), and C, Number of interictal events per 10 min of recording (two-way RM ANOVA, p = 0.404). Data are normalized on their baseline value (pretreatment condition) which is indicated in the plot by the dotted line. Histograms indicate mean ± SEM.
