Fig. 6. SKP1 is required for MPF activity and PI-MI transition during male meiosis.
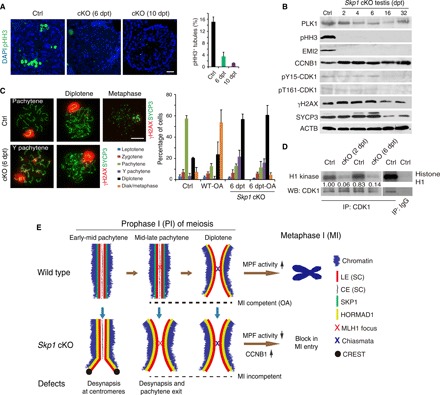
(A) Count of metaphase spermatocytes (pHH3-positive) in seminiferous tubules from WT and Skp1cKO testes. Scale bar, 25 μm. (B) Western blot (WB) analysis of cell cycle regulators in Skp1cKO testes. (C) Skp1-deficient spermatocytes are incompetent for MI entry with OA induction. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Histone H1 kinase assay for the MPF activity in WT (control) and Skp1cKO testes at 2 and 6 dpt. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) serves as a negative control. IP, immunoprecipitation. (E) Key functions of SKP1 during male meiosis. This diagram summarizes the major meiotic defects in Skp1cKO testes. Note the accumulation of HORMAD1 on LEs in Y pachynema and its increased abundance on LEs in diplonema in the absence of SKP1. For illustration purpose, SKP1 and HORMAD1 are shown next to the LEs instead of overlaying.
